Arthroscopy of joints
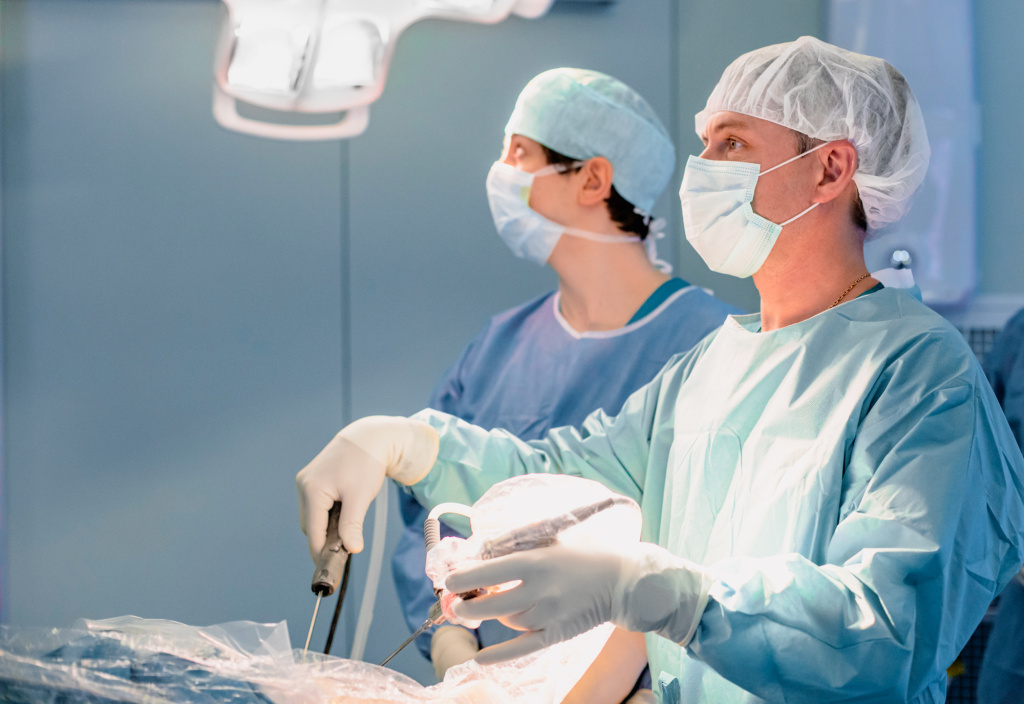
Arthroscopy is a method of diagnosis and treatment of joint pathologies associated with injuries or diseases of intra—articular structures. The method is minimally invasive, access to diagnostic and manipulative instruments is carried out through small punctures, which reduces the likelihood of damage to nerve fibers, blood vessels, and adjacent tissues, and shortens the recovery and rehabilitation time. Arthroscopy is one of the most common orthopedic methods. In the European Clinic of Sports Traumatology and Orthopaedics, arthroscopic operations are performed using modern high-precision equipment by surgeons with many years of experience and experience working abroad. We perform all types of arthroscopic procedures, including operations on the wrist joint.
Types of arthroscopic surgery
Our clinic performs arthroscopic operations on ligaments, tendons, cartilage, menisci, and other soft tissue and bone structures inside joints:
-
Knee joint. Knee joint surgery is often caused by injuries sustained during sports. The most common problems are damage to the menisci, cruciate and lateral ligaments, cartilage, patellar instability;
-
The shoulder joint. A common indication for surgery is a torn rotator cuff, which is typical for throwing and contact sports, as well as for the elderly, when the tendons of the cuff have lost elasticity due to age-related changes.;
-
The ankle joint. Injuries and post-traumatic processes, degenerative pathologies of bone and soft tissues can lead to surgical intervention.;
-
Hip joint. The reasons for surgery are the separation of the articular lip and the pathological proliferation of bone tissue, leading to a decrease in movement volume and pain.
-
Elbow joint. Operations are performed with the proliferation of internal articular membranes, fluid accumulation, intra-articular fractures, degenerative processes, and the presence of free chondral bodies.
-
Wrist joint. Arthroscopy is used to treat tendon ruptures and soft tissue injuries.
Reconstructive surgeries and treatment of acquired and congenital joint pathologies are performed using arthroscopic techniques.
Indications
Indications for diagnostic surgery are cases when a clinical examination, the results of X-ray, MRI and CT examinations do not allow an accurate diagnosis. But in most cases, arthroscopic intervention involves simultaneous diagnosis and treatment. Indications for arthroscopy are:
-
injuries to menisci, ligaments, tendons, and soft tissues;
-
injuries and diseases of the synovial membrane, accumulation of fluid inside the joint;
-
damage and pathology of cartilage, fat body;
-
deforming arthrosis, bone tissue pathology.
Contraindications
Relative contraindications to the operation are:
-
the inability to use anesthesia. Most operations are performed under general anesthesia to ensure long-term immobility of the patient and adequate anesthesia during surgery.
-
infectious inflammation, open wounds in the access area. In this case, the operation may be postponed.;
-
individual characteristics of the patient
In addition, contraindications to surgery may include general contraindications to surgery.
Preparation for the operation
The preparation includes:
-
clinical blood and urine tests;
-
fluorography, ECG;
-
consultations with a general practitioner, an anesthesiologist, an intensive care specialist, and specialized specialists.
In the European Clinic of Sports Traumatology and Orthopedics, a full preoperative examination can be completed within a few hours .
During the consultation before the operation, the doctor must ask the patient about the medications they are taking. It is especially important to inform the specialist about drugs that affect blood clotting, as well as drugs based on the hormone estrogen. These can be hormonal contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy drugs.
No specific training is required. Hospitalization is performed on the day of the operation. At least 6 hours must pass from the last meal and water intake to the operation.
How it goes
Before starting arthroscopy, the patient is anesthetized. The most commonly used ones are:
-
general intravenous anesthesia;
-
epidural (spinal) anesthesia.
The operated area is treated with an antiseptic, after which punctures are performed, and an arthroscope with a camera is inserted into the joint cavity for diagnosis. After the diagnosis, the necessary tools are introduced. To expand the joint, saline solution is fed into its cavity.
The surgeon performs manipulations, after which the instrument is removed, drainage is installed, stitches and sterile wipes are applied to the punctures.
After the operation, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where he will be under the supervision of specialists until he wakes up. When the patient wakes up, they examine him, stabilize his condition and transfer him to a hospital. Most patients spend up to two days in the hospital.
Upon discharge, prescriptions from the attending physician and recommendations from the rehabilitologist are given. Stitches are removed 14 days after surgery.
Rehabilitation
The operation is performed minimally invasively (in a low-traumatic manner), the rehabilitation period proceeds faster, and the patient experiences less pain in the postoperative period.
Rehabilitation in a gentle mode begins immediately after surgery. The rehabilitologist conducts classes in the hospital ward. After discharge, the patient visits the rehabilitation department.
Recovery depends on the amount of surgery, and it can take from several weeks to several months. Classes with a rehabilitologist are aimed at gradually developing an adequate range of movements, reducing pain, and gradually returning to a habitual, active lifestyle.
Make an appointment for a consultation and we will contact you for more details
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses














.webp)




.webp)