Urolithiasis
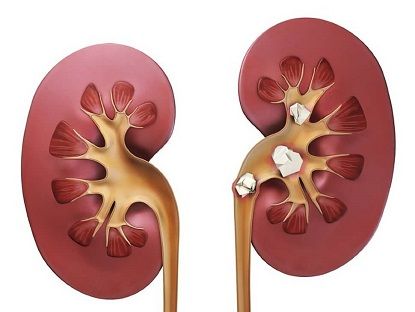 Urolithiasis (ICD) is a disease that is characterized by metabolic disorders with further formation of kidney stones. Among the causes of metabolic disorders leading to the formation of urinary stones, a certain role is played by hereditary/genetic factors (cystinuria, xanthinuria, primary hyperoxaluria, etc.), sedentary lifestyle, malnutrition, insufficient fluid intake, environmental factors (unfavorable composition of drinking water), diseases of the endocrine system (hyperparathyroidism), kidneys (nephrocalcinosis), gastrointestinal tract (Crohn's disease, intestinal malabsorption syndrome, consequences of certain operations), various causes of urinary outflow disorders from the kidneys and bladder (narrowing/stricture of the ureter, ureterocele, vesicoureteral reflux, adenoma prostate gland, etc.). Urinary stones are formed as a result of precipitation and crystallization of salts and organic substances dissolved in urine, and differ in size, location, radiological characteristics (contrast and non-contrast), the causes of their formation and mineral composition.
Urolithiasis (ICD) is a disease that is characterized by metabolic disorders with further formation of kidney stones. Among the causes of metabolic disorders leading to the formation of urinary stones, a certain role is played by hereditary/genetic factors (cystinuria, xanthinuria, primary hyperoxaluria, etc.), sedentary lifestyle, malnutrition, insufficient fluid intake, environmental factors (unfavorable composition of drinking water), diseases of the endocrine system (hyperparathyroidism), kidneys (nephrocalcinosis), gastrointestinal tract (Crohn's disease, intestinal malabsorption syndrome, consequences of certain operations), various causes of urinary outflow disorders from the kidneys and bladder (narrowing/stricture of the ureter, ureterocele, vesicoureteral reflux, adenoma prostate gland, etc.). Urinary stones are formed as a result of precipitation and crystallization of salts and organic substances dissolved in urine, and differ in size, location, radiological characteristics (contrast and non-contrast), the causes of their formation and mineral composition.
Prevalence. About 3% of the world's population suffers from the disease, it is diagnosed in 32-40% of cases of all urological diseases, and is in second place after infectious and inflammatory pathology of the genitourinary organs. It can be detected at any age, but, as a rule, men suffer from this disease 3 times more often than women. Stones often form in one kidney, but in about 15% of cases, urolithiasis is bilateral in nature.
Signs of urolithiasis
Stones can exist asymptomatically for a long time and do not bother a person in any way, being motionless inside the kidney. But when the stone starts to move, it enters the ureter and disrupts the outflow of urine from the kidney. This is accompanied by renal colic: severe, usually unilateral pain in the lower back, extending down the abdomen, sometimes to the groin. With renal colic, the patient searches for, but cannot find, a body position in which this severe pain would be lessened. His behavior is restless. Frequent and false urge to urinate may occur in parallel.
Danger of kidney stones
In the absence of treatment, acute inflammation (pyelonephritis) may develop. Together with renal colic, inflammation can lead to loss of kidney function, or, in other words, to its failure, and in some cases even to death due to the development of a severe infectious process.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic process includes examination by a urologist, collection of a detailed medical history, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the kidneys and urinary tract. The best method of diagnosing urolithiasis is computed tomography (CT), which allows you to identify almost any stones in any part of the urinary tract, determine their exact size and density. In the diagnosis of urolithiasis, it is important to analyze the mineral composition of the stone, which must be performed after its removal in order to carry out measures aimed at preventing the recurrence of the disease.
Treatment
The therapeutic approach depends on the size and location of the stone. With small stones of the ureter, conservative therapy can be carried out, aimed at their independent removal with an indefinite cure period. The modern rhythm of business life sometimes forces patients to choose treatment methods with the fastest possible cure, especially since such methods are well studied, safe and accessible to EMC patients in the world. Modern treatment of urolithiasis is overwhelmingly endoscopic, which allows you to get rid of the stone in one day. In most cases, this treatment is not accompanied by incisions or punctures and is performed using endoscopes guided through the natural urinary tract (through the urethra).
ICD treatment methods used in EMC
Contact ureterolithotripsy is used to remove the ureter stone, in which a thin endoscope is inserted into the ureter, where the stone is destroyed under visual control using laser energy.
If it is necessary to remove a kidney stone, flexible controlled endoscopes are used, allowing you to "look" into the most remote areas of the so-called cup-pelvic system (this is the intrarenal part of the urinary tract, where stones are initially formed). This operation is called retrograde flexible pyelolithotripsy, in which the stones are destroyed in the same way with the help of a laser. We offer these operations to EMC patients with disposable flexible endoscopes.
Only when a large (more than 3 cm) stone grows in the kidneyb, we resort to its removal using percutaneous (percutaneous) nephrolithotripsy, in which the stone is destroyed through a puncture in the lower back. The EMC Urology Clinic is a leader in the treatment of large (coral–shaped) and complicated kidney stones in Russia. In the vast majority of cases, we perform mini-percutaneous nephrolithotripsy when the puncture in the lower back is small (less than 1 cm), which makes the removal of the stone even more gentle, and the hospital stay is short (usually 1-2 days) .
There is a concept of "residual stones" in the endoscopic treatment of urolithiasis. This is the name given to fragments of stones that may remain in the urinary tract after crushing. In the best clinics in the world, this problem exists and residual stones occur with a probability of 3-8%. In the EMC, all patients after endoscopic treatment of urolithiasis are offered a control CT scan to determine the completeness of stone removal.
It is very important for us to maintain trusting relationships with patients!
In order to improve the effectiveness of endoscopic treatment of urolithiasis, we began using augmented reality in the operating room. It should be noted that for the treatment of stones consisting of uric acid salts, there is medicinal litholysis (dissolution of stones). The method allows you to dissolve urate stones without surgery. This technique should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a urologist, since improper treatment can not only fail to dissolve the stones, but also provoke their further growth.A separate important area of our work is help pregnant women.
Metaphylaxis (prevention) of ICD
Urolithiasis recurs very often. If prevention is not carried out, the probability of a new stone appearing in the next five years is 50%. According to the results of the study of the composition of the urinary stone and the identified metabolic disorders, a specific diet is prescribed with a restriction or increase in the intake of certain foods and food components, an increase in the amount of fluid consumed. The identified disorders of the endocrine system are corrected, the identified causes of urinary outflow disorders (urethral stricture, prostate adenoma, ureteral stricture, narrowing of the pelvic-ureter segment) are eliminated, urinary tract infections and vesicoureteral reflux are treated, etc. Preventive measures are an obligatory component of comprehensive treatment of patients and the key to long-term or even complete elimination of the disease.
A team of specialists is able to solve the most difficult tasks and get rid of urinary stones of any localization, size and complexity. The clinic's specialists are ready to help you in an emergency situation, as well as in the implementation of planned surgical and conservative treatment of ICD.
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC



.webp)






.webp)


.webp)
