Plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament
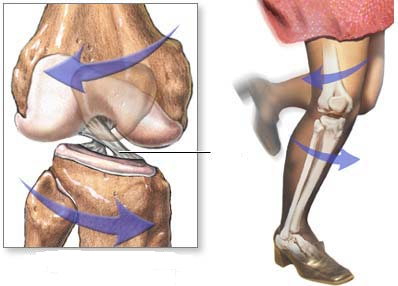 Anterior cruciate ligament rupture is a common injury among athletes and people who lead an active lifestyle. Previously, such damage meant that the function of the knee joint could no longer be restored to its previous level. Today, arthroscopic surgery helps to return to a full life and even pursue a career in professional sports.
Anterior cruciate ligament rupture is a common injury among athletes and people who lead an active lifestyle. Previously, such damage meant that the function of the knee joint could no longer be restored to its previous level. Today, arthroscopic surgery helps to return to a full life and even pursue a career in professional sports.
Anterior cruciate ligament rupture
In the knee joint, the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments act as a stabilizer. They support the shin in the correct position, preventing it from shifting. The posterior ligament is very strong, and it can only be damaged by strong mechanical action. The front is less durable, and its tears and sprains are common.
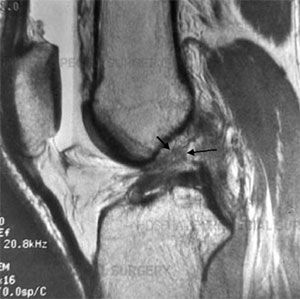 Anterior ligament rupture usually does not require direct impact. This is a typical injury in many sports, when there is a change in direction of movement, a blow when landing or falling. With a sharp internal rotation of the tibia, it shifts anteriorly, which leads to ligament rupture. Sometimes the injury is caused by a direct blow to the shin or thigh.
Anterior ligament rupture usually does not require direct impact. This is a typical injury in many sports, when there is a change in direction of movement, a blow when landing or falling. With a sharp internal rotation of the tibia, it shifts anteriorly, which leads to ligament rupture. Sometimes the injury is caused by a direct blow to the shin or thigh.
Injury symptoms
Immediately at the moment of injury, the victim feels a sharp pain. He may also hear a distinctive crack or click. During the first day, swelling increases. A large amount of blood accumulates in the joint cavity (hemarthrosis), nerve endings are damaged, which makes it impossible to rely on a sore leg.
After the end of the acute period, severe pain is usually not observed. Patients experience discomfort due to joint instability. There may be a feeling that the elements of the knee have shifted relative to each other and are in an unphysiological position. Unpleasant symptoms increase during physical activity, with rotational or sudden movements, as well as during sports.
Rupture diagnostics
An orthopedic traumatologist is involved in the diagnosis of knee ligament ruptures. The doctor collects the patient's medical history, finds out the circumstances of the injury. Then he performs a standard physical examination to assess the condition of the knee joint structures.
Specific tests are used to diagnose PC rupture:
- the "front drawer" test;
- the "pivotshift" test;
- the Lachman test.
During the tests, the doctor asks the patient to take different poses and assesses the degree of forward displacement of the lower leg. This is the main sign indicating a rupture of the anterior ligament. If the nature of the injury is acute, the patient may experience pain, making examination difficult. In this case, before diagnosis, the doctor punctures the joint to remove accumulated blood. This significantly reduces the pain.
Based on the tests, an experienced specialist can already diagnose a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament. But additionally, radiography and MRI are always used. This allows you to identify or exclude concomitant knee joint injuries and confirm the diagnosis.
Indications and contraindications for surgery
In the acute period of injury, painkillers and cold compresses are prescribed to relieve swelling. If hemarthrosis is present, the joint is punctured, removing the accumulated blood. The injured limb is immobilized for 5-7 days using orthoses. When the unpleasant sensations pass, it is allowed to perform habitual movements, lean on the injured lower limb.
The rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament itself is not a direct indication for surgery. Joint instability is crucial. If the patient feels knee instability, lower leg dislocation, or twisting, this requires surgical treatment. The torn ligament fibers themselves cannot heal due to insufficient blood circulation in this area.
Indications for surgical treatment of injury are:
-
joint instability with any degree of ligament rupture;
-
complete separation of the ligament from the femur or tibia;
-
concomitant damage to other joint structures;
-
partial rupture of the control panel.
In some cases, surgery is contraindicated. Surgical intervention is not performed if the patient has a history of:
-
severe pathologies of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and excretory systems;
-
trophic lesions, purulent dermatitis in the surgical area;
-
serious concomitant diseases: diabetes mellitus, oncology, disorders of the blood coagulation system;
-
persistent knee contracture;
-
progressive arthrosis of the knee joint.
Some of the contraindications are relative. They can be eliminated by undergoing appropriate treatment, after which the patient will be admitted to surgery.
Arthroscopic plastic surgery
In case of rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament during surgical treatment, suturing of damaged tissues is usually not performed. This is often technically impossible to do. Refixation of the anterior cruciate ligament is a possible option, but it is rarely done. Since it is impossible to sew a bundle, it needs to be replaced. Outrotransplants (from the patient's own tissues) or allografts (from other people's tissues) can be used for this purpose. Nowadays, donor tissues are practically not used.
The gold standard of treatment is reconstruction using an autograft (most often from the tendons of the muscles of the posterior surface of the thigh) and biodegradable fixators. The operation is performed arthroscopically. This means that surgery is performed minimally invasively. The joint is not fully opened, but the necessary manipulations are performed through two small incisions.
The operation is more often performed under spinal anesthesia. If it is contraindicated in the patient, spinal anesthesia may be used. The procedure lasts about 1-2 hours. Arthroscopic ligament reconstruction consists of several stages:
- Removal of the remaining part of the ligament.
- Tissue sampling for reconstruction. The doctor chooses the most appropriate place for tendon removal, depending on the patient's medical history.
- Preparation of the autotransplat. The tendon is cleaned, folded and stretched before installation.
- Drilling a channel in the bones to accommodate the graft.
- Fixation of the graft using biodegradable (self-absorbable) screws. In some cases, titanium retainers are used. After healing, the autograft grows into the bone at the attachment points.
During the operation, the doctor also necessarily treats concomitant knee joint injuries, if any.
Arthroscopic reconstruction using an autograft completely restores joint function in more than 90% of cases. Own tissues take root well, and minimally invasive access promotes rapid recovery. It is also important that no significant scars remain after arthroscopy. Incisions are almost invisible after healing.
Possible complications
Minimally invasive arthroscopic intervention reduces the risk of postoperative complications. However, some patients have the following symptoms:
-
Postoperative infections. They can lead to osteoarthritis and other serious consequences.
-
Limitations of knee joint mobility (contracture).
-
The proliferation of scar tissue in the joint (arthrofibrosis).
-
Pain in the area of graft tissue collection.
It is also possible to rupture the graft or detach it from the bone channels. In this case, the operation is considered unsuccessful, and a second intervention (revision) is performed. Gradual recovery under the guidance of a rehabilitation specialist and compliance with your doctor's recommendations helps to reduce the risk of complications.
Postoperative recovery
In the first days after surgery, drug therapy is used to reduce swelling and control pain. Measures are also being taken to relieve swelling. Cold compresses and the position in which the operated lower limb is raised are shown. To immobilize the joint, a brace is used to fix the limb in full extension. During the entire recovery period, the patient should use crutches to relieve stress on the knee joint.
During the recovery period, the patient is under the supervision of a rehabilitologist. He prescribes physical therapy exercises with a gradual increase in workload. The main task at this moment is to maintain the tone of the thigh and shin muscles, since muscle mass is quickly lost during the period of immobilization. Exercises are also performed to restore the mobility of the patella and postoperative scar.
You can return to sports activities no earlier than in six months. Professional athletes often return to training after 3-4 months. The exact date can only be announced by a doctor after a control isokinetic test. It is important that the thigh muscles of the operated lower limb achieve satisfactory strength compared to the healthy one.
If you are concerned about pain, swelling, or instability in the knee joint, make an appointment for an examination at the EMC clinic. Each patient is guided by a whole team of doctors: traumatologists, orthopedists, rehabilitologists. All knee joint pathologies without treatment lead to serious complications, including the need for endoprosthetics (replacement with an artificial implant). At the same time, timely medical intervention helps to fully restore the functions of the joint.
Links to expert sources
- Algorithm of medical rehabilitation of patients after anterior cruciate ligament surgery
- Clinical efficacy of anatomical plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint
References
- Korolev A.V., Ryazantsev M.S., Magnitskaya N.E., Afanasyev A.P., Ilyin D.O., Frolov A.V. Long-term results of meniscus suturing during arthroscopic plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament // Traumatology and orthopedics of Russia. 2016. №3.
- Ryazantsev Mikhail Sergeevich, Magnitskaya Nina Evgenievna, Zaripov Aziz Rimovich, Logvinov Alexey Nikolaevich, Ilyin Dmitry Olegovich, Afanasyev Alexey Pavlovich, Frolov Alexander Vladimirovich, Korolev Andrey Vadimovich Anthropometric data and cross-sectional area of tendons of semi-tendon and tender muscles according to MRI data as predictors of graft diameter for plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament // Genius of Orthopedics. 2021. №2.
- Yasen S. K. et al. Clinical outcomes of anatomic, all-inside, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction //The Knee. – 2017. – Vol. 24. – No. 1. – pp. 55-62.
- Nina Evgenievna Magnitskaya, Mikhail Sergeevich Ryazantsev, Musa Nazirovich Maisigov, Alexey Nikolaevich Logvinov, Aziz Rimovich Zaripov, Andrey Vadimovich Korolev Translation, validation and cultural adaptation of the IKDC 2000 subjective knee form orthopedic questionnaire for assessing the condition of the knee joint. 2019. №3. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/perevod-validatsiya-i-kulturnaya-adaptatsiya-ortopedicheskogo-opro... (accessed 04.04.2023).
- Kaplan Y., Witvrouw E. When is it safe to return to sport after ACL reconstruction. Reviewing the criteria //Sports health. – 2019. – Vol. 11. – No. 4. – pp. 301-305.
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC














.webp)




.webp)
