Rotator cuff rupture
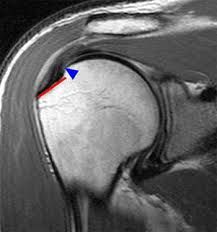 The rotator cuff is a complex of four muscles and tendons that coordinate movements in the shoulder joint. These include the supraspinatus, subacute, subscapular, and small round muscles. They are dynamic stabilizers of the shoulder joint, centering the head of the humerus in the articular cavity of the scapula, and perform external and internal rotation of the shoulder.
The rotator cuff is a complex of four muscles and tendons that coordinate movements in the shoulder joint. These include the supraspinatus, subacute, subscapular, and small round muscles. They are dynamic stabilizers of the shoulder joint, centering the head of the humerus in the articular cavity of the scapula, and perform external and internal rotation of the shoulder.
Rotator cuff injuries are a common cause of pain and limited movement in the shoulder joint. Among those who have come forward with this problem, there are both young patients who are actively involved in sports, and elderly people.
The causes of rotator cuff injuries vary in these age groups. Young patients often have a history of sports or professional activities related to the elevated position of the arm and throwing movements. The most common sports are volleyball, baseball, and tennis. Constant microtraumatization of the rotator cuff tendons during ball strikes, serves, and throws can lead to tendonitis as manifestations of overuse syndrome. As a result, biomechanical relationships in the joint are disrupted and pain syndrome occurs. In the future, even a small injury becomes enough to cause a tendon rupture and, as a result, limit active movements. In some cases, the rupture of the rotator cuff tendons occurs simultaneously under the influence of a high-force traumatic agent, often during dislocation in the shoulder joint.
Elderly people develop gradual age-related degeneration of the rotator cuff with a characteristic pain syndrome, sometimes a complete rupture clinic is observed.
Tendinitis and incomplete ruptures of the rotator cuff are manifested by pain in the upper arm, which increases with movement, and night pains are possible. With complete ruptures, the main complaint is the restriction of active movements – the inability to withdraw the hand without assistance. Patients who come forward with such complaints need a detailed clinical examination, as well as radiography, ultrasound, and MRI to accurately identify damaged muscles and tendons, as well as a differential diagnosis with other conditions accompanied by these symptoms.
In case of inflammatory changes in the rotator cuff, it is advisable to limit physical activity, analgesics, physiotherapy, exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the shoulder girdle. Young patients with an established diagnosis of rotator cuff rupture are indicated for surgical intervention – open or arthroscopic suturing as early as possible after injury. In elderly patients, conservative treatment is used, sometimes arthroscopic revision and decompression of the subacromial space (the area where the tendons are pinched, see "subacromial impingement syndrome") is indicated.
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC














.webp)




.webp)
