Rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament
 A torn posterior cruciate ligament is a serious injury that can lead to the formation of posterior instability and constant pain in the knee joint. But thanks to modern treatment methods, patients return to an active life even after such an injury. The EMC clinic uses various treatment methods, including conservative and surgical, depending on the severity of the injury and the presence of concomitant injuries.
A torn posterior cruciate ligament is a serious injury that can lead to the formation of posterior instability and constant pain in the knee joint. But thanks to modern treatment methods, patients return to an active life even after such an injury. The EMC clinic uses various treatment methods, including conservative and surgical, depending on the severity of the injury and the presence of concomitant injuries.
What is a gap in the ZKS
The posterior cruciate ligament serves as a stabilizer of the knee joint, preventing the lower leg from moving backwards. This is a strong structure made of collagen fibers, but it can rupture under high traumatic stress. As a result of the rupture, joint instability is formed. Patients with such an injury experience pain, their movements are disrupted, and often a person cannot even walk normally.
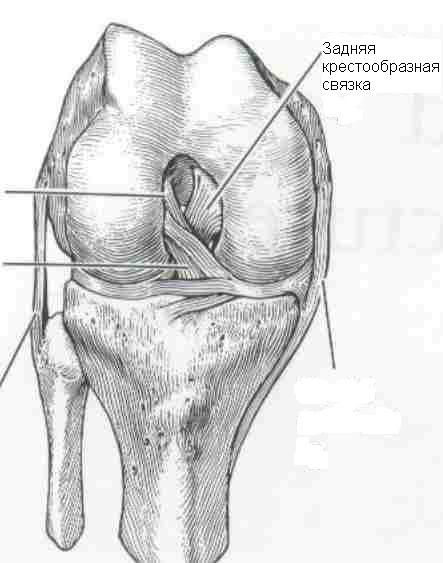
The posterior ligament is very strong, consists of two bundles, and it is quite difficult to damage it. This can happen with a strong directional blow to the upper third of the shin. It is almost impossible to keep other structures of the knee joint intact under such influence. Therefore, in 90% of cases, SCL ruptures occur simultaneously with other injuries.
Ruptures of the posterior cruciate ligament are classified according to the degree of damage:
-
Partial rupture. Incomplete destruction of the structure. The stability of the joint is still preserved, but the likelihood of repeated injury increases due to a decrease in ligament strength.
-
A complete breakup. The ligament does not perform its function, the stability of the joint is impaired. At this stage, the victim cannot lean on the injured leg.
If the patient does not receive timely treatment, the condition may worsen. Chronic ligament damage can lead to serious complications. These are recurrent joint instability, deforming gonarthrosis, and patellofemoral arthrosis.
Causes of ruptures
The posterior cruciate ligament is a strong structure that ruptures mainly due to a high−energy injury mechanism. In everyday conditions, the probability of such a gap is much less. Injury usually occurs in the following situations:
-
Traffic accident. Typical damage occurs as a result of emergency braking, when the shin hits the dashboard. A pedestrian who has been hit or a motorcyclist who has fallen can also get a break.
-
Some sports. A rupture of the SCL can occur with a sharp blow to the shin, for example, when players collide in contact sports (rugby, football). Skiers who crash into obstacles at high speed also suffer from injury.
-
Non-contact injury mechanism. The reason is the structural features of the musculoskeletal system or degenerative changes in the joint. For example, in patients with hyperflexia or hyperextension (excessive movements) in the joint.
Since the SCLC usually tears due to strong mechanical stress, many patients experience combined injuries. These are often dislocations, injuries to other ligaments of the knee joint, sprains, fractures of other structures of the knee joint.
Symptoms of the disease
At the moment of rupture of the ligament, the victims experience severe pain. Due to mechanical action, the surrounding vessels are destroyed, edema (hemarthrosis) occurs. Patients may also observe a bruise spreading along the back of the shin.
Another symptom is joint instability. The patients' ability to move is limited, and gait disorders are noted. Often, the patient cannot even step on the injured limb and use it in walking.
The symptoms associated with a cruciate ligament rupture are nonspecific and occur with many other injuries of the musculoskeletal system. Diagnosis of SCL rupture requires highly qualified orthopaedic surgeon and the use of specialized research methods. An independent attempt to diagnose or treat a disease can lead to serious consequences.
Diagnostics
A cruciate ligament tear is usually the result of high-energy injuries. As a rule, such patients have other injuries, so most of the victims seek help in a hospital or emergency room. But even with this, a ligament tear is often not diagnosed.
Diagnosis can be difficult due to pain in the acute period, especially in the presence of concomitant injuries. Orthopedic traumatologists use special tests to make an accurate diagnosis:
-
The "back drawer" test;
-
The Clancy symptom test;
-
The Godfrey test;
-
quadriceps muscle test.
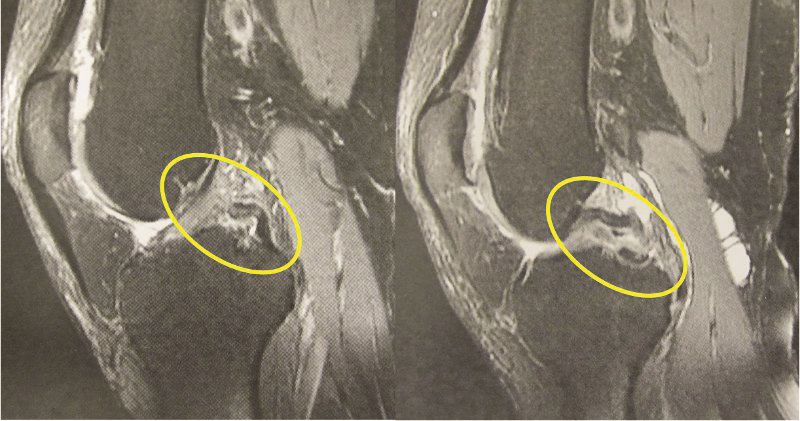
Radiographs and MRI scans are also used for diagnosis. An X-ray allows you to identify fractures and bone tears, assess the condition of the articular gap and the congruence of articular surfaces. Magnetic resonance imaging helps to identify the rupture of the cruciate ligament as effectively as possible, especially in the acute period.
Conservative treatment of rupture
The posterior cruciate ligament is located in the area of good blood circulation, mostly outside the joint. Therefore, conservative therapy is actively used for incomplete ruptures. When choosing the right orthosis and observing the timing of immobilization, the torn fragments fuse on their own, which avoids surgical intervention. Conservative therapy is also indicated in the general serious condition of the patient, for example, in the presence of other injuries after an accident.
Here are the indications for conservative treatment:
-
partial rupture of the cruciate ligament;
-
the posterior displacement according to stress radiography is less than 10 mm.
Conservative treatment always involves immobilization and stress relief from the injured knee. Immobilization is performed in a specialized orthosis with posterior shin support in an upright position for 3 weeks, then replaced with a dynamic articulated orthosis also with posterior shin support. The patient should move with the help of crutches. Doctors also prescribe drug therapy: painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors.
Operation in case of rupture of the ZKS
Surgical treatment is used in case of complete rupture, as well as damage to other ligamentous and bony structures of the knee joint. The operation is also performed for athletes: it is the only one that helps to completely restore the ligament structure, which is especially important for professional achievements. Surgical treatment is also resorted to after conservative therapy, if it has not been possible to achieve an effect with its help.
To date, the restoration of the ZKS has been carried out with open access, but the results of treatment have been unsatisfactory. In this regard, at the moment the reconstruction of the ZKS is carried out by arthroscopic method.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery. Surgical treatment is performed through 2 small punctures in the knee joint area. An arthroscope is inserted through the first one: a device for broadcasting an enlarged image to a monitor. The necessary surgical procedures are performed through the second puncture under full visual control.
To treat a cruciate ligament tear, doctors perform:
-
arthroscopic plastic surgery with a free autograft;
-
augmentation (reinforcement) with synthetic threads.
The treatment strategy is chosen by an orthopedic traumatologist, taking into account the patient's medical history.
Recovery and rehabilitation
Immediately after surgery, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy. Cooling compresses and painkillers are used to relieve swelling and pain. The limb is immobilized in an orthosis with posterior shin support. As part of the postoperative protocol, it is necessary to use additional support (crutches).
In the postoperative period, a recovery program is formed together with a rehabilitologist. Physical therapy is mandatory, and the doctor may also prescribe physical therapy. The load is increased gradually, under the constant supervision of a specialist. When the leg's ability to support itself is restored by three quarters, the patient is allowed to switch to one crutch. You can walk on your own after full restoration of joint function. Active activities and sports are allowed after an average of 6 months.
There are no specific ways to prevent ruptures. It is recommended to follow standard safety measures, perform joint warm-ups before exercising, and adhere to proper exercise techniques.
With timely treatment, the prognosis for patients with ligament injuries is favorable. But in his absence, complications are inevitable in the future. The most severe of these is osteoarthritis of the knee joint, which may require replacement of the joint with an artificial one. If you are concerned about knee pain, make an appointment for an examination at the EMC clinic. Our traumatologists and orthopedists work with acute, chronic and long-standing injuries, and will help restore joint mobility even in the most difficult cases.
Links to expert sources
-
Pache S. Posterior Cruciate Ligament: Current Concepts Review // Pache S. Aman Z.S., Kennedy K.M., Nakama Y.G., Moatshe G., Ziegler C., LaPrade R.F. The Archives of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2018. № 1 (6). C. 8–18.
-
Feshchenko Dmitry Evgenievich, Moskalenko Igor Sergeevich, Koryukhin Maxim Alekseevich The use of physical therapy for rupture of the cruciate ligaments of the knee joint // Symbol of Science. 2017. №3.
-
Chahla J. Posterolateral corner of the knee: an expert consensus statement on diagnosis, classification, treatment, and rehabilitation // Chahla J., Murray I.R., Robinson J., Lagae K., Margheritini F., Fritsch B., Leyes M., Barenius B., Pujol N., Engebretsen L., Lind M., Cohen M., Maestu R., Getgood A., Ferrer G., Villascusa S., Uchida S., Levy B.A., Bormann R.V., Brown C., Menetrey J., Hantes M., Lording T., Samuelsson K., Frosch K.H., Monllau J.C., Parker D., LaPrade R.F., Gelber P. E. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 2019. № 8 (27). C. 2520–2529.
-
Bedi A. Management of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries: An Evidence-Based Review // Bedi A., Musahl V., Cowan J. B. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2016. № 5 (24). C. 277–289.
-
Strobel (Manual of arthroscopic surgery / M. Strobel : translated from English. edited by A.V. Korolev. Moscow : Panfilov Publishing House ; BINOM. Laboratory of Knowledge, 2012. – 672 p.).
-
Korolev A.V. Posterior cruciate ligament injuries: biomechanics, main directions of diagnosis, treatment and prevention of secondary osteoarthritis / Korolev A.V., Afanasyev A.P., Ilyin D.O., Zaripov A.R., Ryazantsev M.S. // Surgery. The N.I. Pirogov Magazine. – 2020. – No. 9. – pp. 130-136
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC














.webp)





