Meniscus rupture
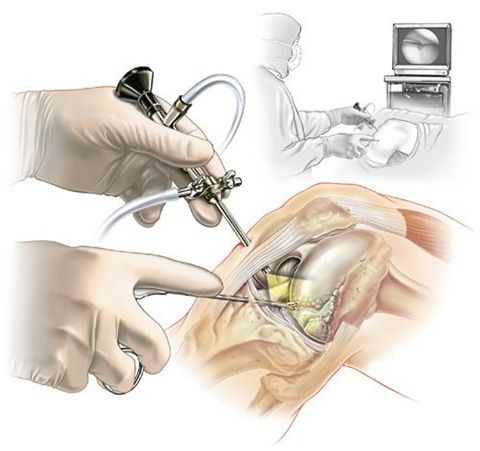 Meniscus tear is the most common knee injury. This damage is typical for both young, active people and older people. The rupture causes acute pain, swelling, and limitations in movement, including the inability to bend and straighten the knee joint. Depending on the degree of rupture, treatment is performed using conservative or surgical methods.
Meniscus tear is the most common knee injury. This damage is typical for both young, active people and older people. The rupture causes acute pain, swelling, and limitations in movement, including the inability to bend and straighten the knee joint. Depending on the degree of rupture, treatment is performed using conservative or surgical methods.
What is a meniscus tear
The meniscus is a cartilaginous structure that acts as a shock absorber and stabilizer for the joint. There are two of them in each knee joint: the inner meniscus (medial) and the outer (lateral). The meniscus is C-shaped, and its ends are called the anterior and posterior horns.
The meniscus may rupture at the moment of sudden non-physiological movement. When the joint moves, the meniscus stays in place, resisting. If its integrity is violated, the torn part is displaced, which leads to severe pain. The posterior horn is most often injured, but ruptures in other areas are also possible. The internal meniscus is connected to the capsule of the knee joint, so combined injuries are common.
The meniscus may be completely torn off or partially torn. Traumatologists use several classifications to describe pathology:
-
by type of gap: combined;
-
by circulatory zones: red, pink, white;
-
by the presence of a gap offset;
-
by severity (Stoller classification).
A meniscus tear is one of the most common injuries of the musculoskeletal system. Men are more susceptible to it than women. The older a person is, the more pronounced his degenerative changes in bone tissue are. The frequency of injury in the elderly is also related to this.
Symptoms of meniscus injury
The moment of injury is often characterized by sharp and severe pain, but this is not necessary. The symptoms depend on the location of the injury and its severity. With partial ruptures, patients experience discomfort when moving, and with complete ruptures, they are even more limited in walking. Usually, patients note:
-
pain in the knee joint area;
-
edema;
-
limited movement up to complete blockage (jamming);
-
hip muscle hypotrophy;
- specific sounds when moving (cracking, clicking).
Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor immediately. If you do not start treatment immediately after the injury, the meniscus damage becomes chronic (long-standing). Unpleasant symptoms persist for a long time, and any awkward movement can lead to repeated damage. With each subsequent injury, the size of the meniscus tear will increase.
Causes of occurrence
The most common cause of meniscus rupture is a sharp rotation of the shin relative to the hip. This situation can happen to anyone. An unsuccessful fall, injury, road accident, and sports often cause illness. At the same time, some people are potentially at risk:
-
people who play sports with rapid changes of direction (football, basketball, volleyball, skiing, figure skating);
-
overweight patients due to increased stress on the joints;
-
older people due to degenerative processes;
-
persons with congenital disorders of the anatomical relationship of knee structures;
-
professions that are characterized by kneeling or lifting weights.
Between the ages of 20 and 40, meniscus tears usually occur due to injury. After 40, degenerative-dystrophic processes come out on top, in which it is much easier to get damaged. Often, older patients do not even notice injuries or falls that could lead to rupture.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to determine the meniscus rupture on your own. This diagnosis is made only by a doctor, usually an orthopedic traumatologist. The standard procedure begins with the collection of medical history. The specialist asks the patient about the nature of the pain, possible causes of its occurrence, and existing concomitant diseases. Then the doctor proceeds to the examination.
The specialist examines the condition of the lower extremities, not just the painful area. Special diagnostic tests help to assess the amplitude and painfulness of movements in the knee and hip joints. It is important to determine if muscle atrophy has occurred. The doctor also examines the joint for effusion. It indicates an accumulation of fluid: hemarthrosis with fresh lesions, and synovitis with old ones.
An experienced doctor can make a diagnosis already at this stage, but hardware methods are used to confirm it:
-
radiography in several projections to assess the condition of bone structures, the stage of osteoarthritis;
-
An MRI scan is used to obtain an accurate image of the internal structures of the ligaments and menisci, and to determine the nature and location of the rupture.
In some cases, arthroscopy is also performed. This is a minimally invasive surgery for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The doctor may prescribe a procedure to eliminate the pathology. The operation is performed only for medical purposes only if there are indications.
Meniscus rupture treatment
The treatment strategy is selected depending on the degree of meniscus damage, as well as the patient's complaints. The doctor can use both conservative and surgical techniques. A combination of different therapeutic tactics is also often used.
Conservative treatment is prescribed for small ruptures of the posterior horn of the meniscus or minor radial tears. In conservative treatment, rest of the injured limb is important. The doctor can prescribe different options for action: from complete immobilization for 7-10 days to soft bandaging or wearing orthoses. The elevated position of the lower limb is shown.
In addition to limiting mobility, other methods are used in conservative treatment:
-
puncture to remove accumulated fluid;
-
cold compresses to relieve swelling;
-
drug therapy (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors);
-
physical therapy.
If the meniscus rupture is large, or there is a blockage (jamming) of the knee joint, or conservative treatment does not work, surgical methods are used. For example, this is a necessary measure when the posterior horn of the meniscus is completely detached.Arthroscopy is most often used. This minimally invasive procedure is characterized by low trauma, so patients recover quickly and return to their usual lives.
Arthroscopy is performed through two micro-incisions. An arthroscope is inserted into one, an optical device for displaying a magnified image on a monitor. Surgical instruments are placed in the second incision, with which the doctor performs the necessary manipulations.
Depending on the depth and type of rupture, the surgeon decides whether to stitch or resect the damaged part. Suturing is considered the optimal method in terms of meniscus preservation, but it is not shown in all cases. During resection, only damaged areas that no longer perform their function are removed. The surgeon also restores the smooth inner edge of the meniscus.
Recovery and rehabilitation
Immediately after arthroscopy, the doctor may prescribe pain medications to prevent complications and relieve pain. Cold compresses are also used to reduce swelling of the tissues.
After the operation, the rehabilitation program is prepared by a rehabilitologist. The very next day, the patient begins to perform physical therapy exercises, with a gentle and gradual increase in activity. At first, walking may require crutches. Usually, the full load on the limb is allowed the next day after surgery, but when the meniscus is stitched, rehabilitation is prolonged.
Full recovery may take from 1 to 3 months, depending on the severity of the disease. It is important to follow all the prescriptions of the attending physician and rehabilitologist in order to return to an active life as soon as possible. Special exercises and physical therapy will help recovery.
Rupture prevention
After the end of the recovery period, the patient can return to normal life. Orthopedic traumatologists do not impose categorical prohibitions on any type of activity, but it is important to remember about the injury and follow basic safety measures. Recommended:
-
Strengthen the muscles that support the joint in the correct anatomical position. Special exercises prescribed by a rehabilitologist will help.
-
Take time to warm up before any sports activities. This is an important part of injury prevention.
-
Increase sports and household activities gradually.
-
Reduce the risk of injury: avoid dangerous sports, move carefully on slippery surfaces, and avoid physical impacts on the knee area.
-
Maintain a healthy weight. Excess body weight increases the stress on the joints.
If you experience any discomfort in the knee joint area, you should consult a doctor. Regular follow-up with an orthopedic traumatologist is also recommended to monitor the condition of the musculoskeletal system.
Meniscus ruptures are successfully treated, but it is important to consult a doctor in time to prevent the disease from becoming chronic (long-standing). The EMC clinic is attended by experienced orthopedic traumatologists, and modern minimally invasive methods can help the patient quickly return to his usual lifestyle. Make an appointment with a doctor to get rid of the pain and return to an active life without restrictions in movement.
Links to expert sources
References
-
Korolev A.V., Ryazantsev M.S., Magnitskaya N.E., Afanasyev A.P., Ilyin D.O., Frolov A.V. Long-term results of meniscus suturing during arthroscopic plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament // Traumatology and orthopedics of Russia. 2016. №3. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/otdalennye-rezultaty-sshivaniya-meniskov-pri-artroskopicheskoy-pla... (accessed 04/04/2023).
-
Abram, S. G. F., Beard, D. J., Price, A. J., & BASK Meniscal Working Group. (2019). Arthroscopic meniscal surgery: a national society treatment guideline and consensus statement. Thebone&jointjournal, 101(6), 652-659.
-
Ryazantsev, M. S., Magnitskaya, N. E., Ilyin, D. O., Afanasyev, A. P., Frolov, A.V., & Korolev, A.V. (2018). The history of the development of meniscus suturing methods (review of foreign literature). Bulletin of Traumatology and Orthopedics. NN Priorova, (1), 72-79.
-
Ryazantsev M. S. Reconstructive surgery of the menisci in plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament long-term results : dis. – Russian University of Friendship of Peoples, 2017.
-
Kurzweil PR, Cannon WD, DeHaven KE. Meniscus Repair and Replacement. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2018 Dec;26(4):160-164. doi: 10.1097/JSA.0000000000000224. PMID: 30395058.
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC














.webp)





