Rosacea - symptoms and treatment options at EMC
It is localized mainly on the face: in the area of the forehead, nose and chin. Rarely - on the neck, chest, scalp or ears.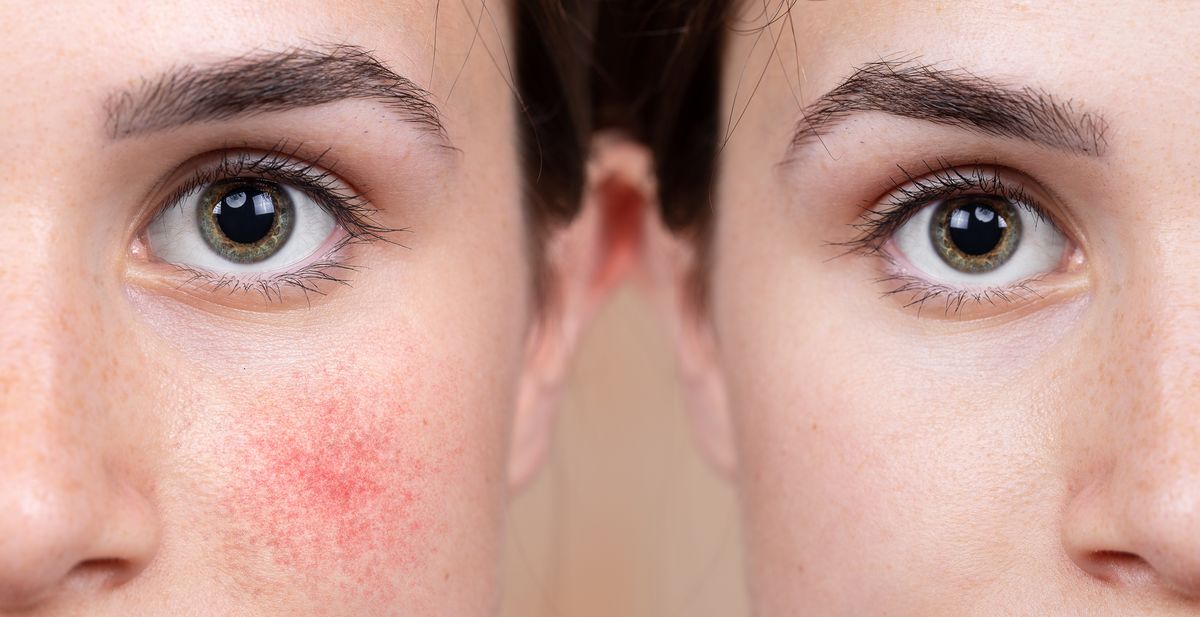
Locations of rosacea:
-
Face: cheeks, nose, zygomatic arches, chin and mouth area, forehead, eyebrows, conjunctiva of eyes and eyelids
-
The scalp
-
Auricles
-
Cleavage area
-
Epigastric region (extremely rare)
Rosacea: learn more about the disease
Rosacea is a genetic condition of the skin, an individual feature of the vascular structure and their reactivity. Rosacea accounts for 5-7% of all dermatoses in Russia, but the number of such patients has increased recently.
Often, the patient does not even suspect that he has a disease, because the symptoms are similar to rashes. The difficulty in this case lies in the fact that acne and rosacea can exist in one person at the same time. The only thing is that acne is more common at a younger age, and rosacea is more common in people between the ages of 30 and 50. Acne goes away with age, but rosacea cannot "outgrow".
Rosacea affects both men and women equally. In men, it is less common, but occurs in a more severe form. The disease is rare in children.
Causes of rosacea
The exact causes of rosacea have not yet been established. One of the main versions is that the disease is genetically determined and occurs due to changes in the tone of superficially located small vessels (arterioles).
Factors that influence the occurrence of rosacea exacerbations:
External factors:
-
abuse of spicy food and spices
-
consumption of hot drinks (60 and above)
-
chemical peels
-
the use of drugs with corticosteroids (steroid rosacea)
-
cosmetics with aggressive ingredients
-
taking certain medications
-
excessive insolation, UV radiation
-
strong wind
-
exposure to high and low temperatures
-
alcohol abuse
Internal factors:
-
diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic, gastritis, chronic colitis, chronic cholecystopancreatitis)
-
endocrinological pathologies
-
disorders of the immune system
-
the first and second types of Fitzpatrick photosensitivity
-
neurovegetative and microcirculatory disorders
-
functional insufficiency of peripheral blood supply
Rosacea most often manifests itself in 30-40 years. After 40 years of age, the manifestation of symptoms in women is often associated with menopause. After the age of 50 and in childhood, the primary development of the disease is extremely rare.
A genetic factor plays an important role in the development of the disease. Rosacea may be associated with the peculiarities of the vascular structure or the functioning of various body systems that affect the formation of this condition. Studies have shown that in 40% of cases, relatives of patients have a history of the disease.
Classification of rosacea
Despite the fact that rosacea is a chronic disease with periods of exacerbations and remissions, there are five stages of the pathological process development:
-
Transient erythema of the central part of the face. Short-term episodes of redness that occur suddenly and disappear without consequences.
-
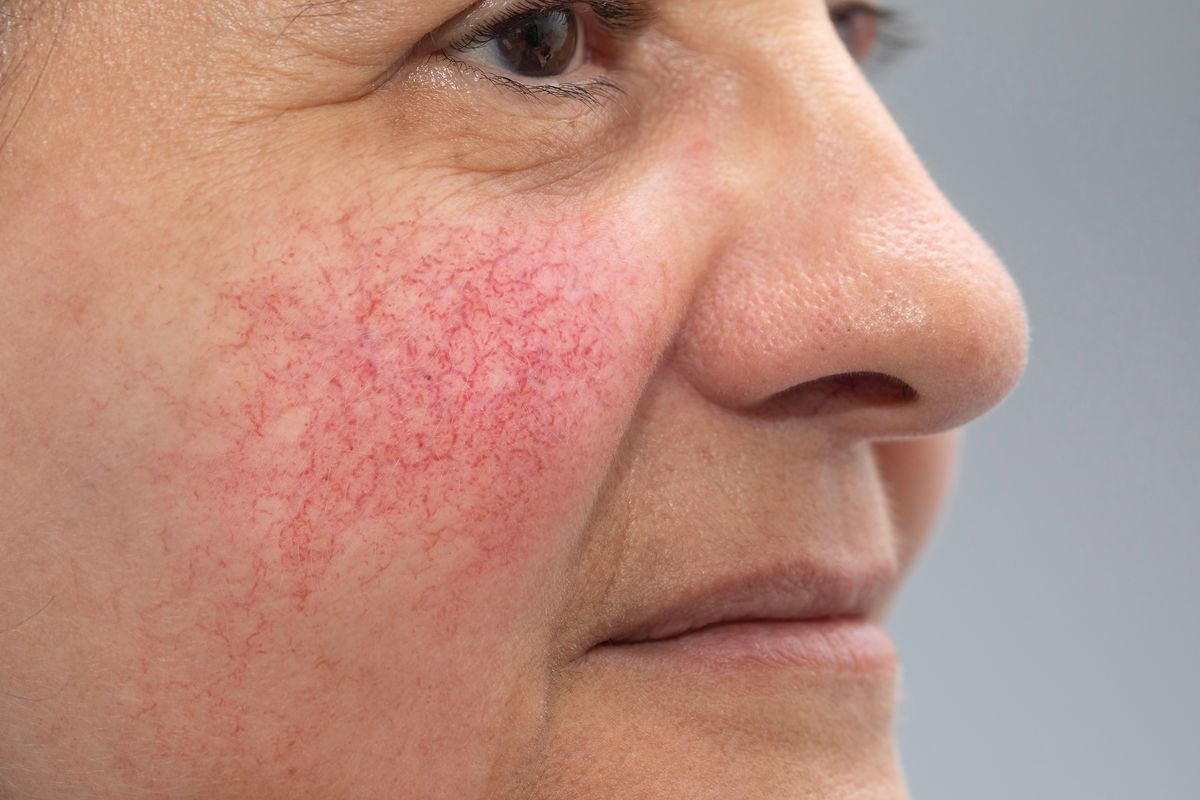
Persistent (background) erythema and telangiectasia. They develop due to the expansion of the vascular network after numerous cases of transient erythema.
-
Papular stage. Papules begin to form on the skin.
-
Pustular stage (pustules appear).
-
Infiltrative-productive stage. Edema and fibroto-hypertrophic changes in the skin appear.
There are four subtypes of rosacea:
-
Erythematous-telangiectatic rosacea. It is distinguished by the presence of transient erythema, turning into persistent, telangiectasia and swelling.
-
Papulo-pustular rosacea. It is characterized by the formation of papules and pustules on the skin.
-
Phymatous rosacea is characterized by thickening of the skin, the appearance of a characteristic bumpy surface and the appearance of pineal growths in the nose, on the forehead, on the chin, on the auricle, on the eyelid.
-
Ophthalmorosacea. It can occur at any stage of the disease (possibly even before the appearance of skin symptoms) and is characterized by various eye pathologies. More often it is blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids) or conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye). In some cases, meibomyitis (inflammation of the meibomian glands located on the edges of the eyelids) and recurrent chalazion. In difficult cases, keratitis, scleritis and iridocyclitis develop.
Atypical forms of rosacea
-
Granulomatous (lupoid). It is characterized by the appearance of dense yellowish papules (granulomas), which, after opening, can leave scars on the skin.
-
Conglobate. Large nodules with signs of the spread of purulent process and fistulas appear.
-
Halogen. It develops as a result of taking iodine and bromine preparations, the symptoms are similar to the conglobate form.
-
Steroidal. Occurs due to prolonged use of local steroid medications.
-
Gramnegative. It can develop as a result of incorrect antibacterial therapy, and is characterized by the addition of gram-negative microorganisms.
-
Fulminant. It is characterized by a sudden and rapid development of symptoms, including edema, hyperemia, papulo-pustular formations with purulent discharge.
Symptoms of rosacea
The manifestations of the disease depend on the stage of development of the disease.
-
Erythematous stage. Areas of hyperemia on the face (forehead, nose, cheeks), rarely on the chest, and telangiectasia appear and may persist for several days. Gradually, the number of seizures of hyperemia and their duration increase.The hyperemia becomes brighter, sometimes it takes on a bluish tint. There is swelling and peeling. The patient feels a burning sensation at the site of the symptoms.
-
Papular (pustular) stage. In parallel with hyperemia, multiple grouped small papules or pustules with thin whitish scales appear. The main localization is the nose and nasolabial folds, followed by spreading to the chin and forehead. The symptoms persist for several weeks.
-
In difficult cases, skin swelling may appear, most often in the area between the eyebrows. The patient does not experience any discomfort, except for severe itching when the process spreads to the scalp. A rash may appear on the chest or on the back.
-
At the papular nodular stage, there is an increase and fusion of the elements of the rash, this process is accompanied by the formation of nodes and plaques. Hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands is possible, followed by fibrosis. The effect of an "orange peel" is observed on the skin, the tuberosity gradually leads to a change in the shape of the nose, ears, and forehead relief.
Classification of atypical forms of rosacea on the face
-
Granulomatous (lupoid) form: reddish-brown papules 2-4 mm with clear borders, localized in the mouth and eyes. They can be singular or plural.
-
Conglobate shape: large nodes up to 2 cm, with a brown or bluish tint.
-
Fulminant form: sudden appearance of multiple elements: papules, pustules, nodules. Edema and hyperemia with a bluish tinge are characteristic. The predominant localization is the forehead, chin, and cheeks. It is severe and difficult to treat.
-
Lymphoedema: cyanotic erythema and swelling of the middle part of the face associated with the proliferation of connective tissue as a result of chronic inflammation. It is very rare.
-
Ophthalmorosacea: the eyes are involved in the inflammatory process, keratitis, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, chalazion, etc. develop.
Diagnosis of rosacea
The necessary diagnostic techniques are determined as a result of a detailed consultation with a dermatologist, medical history collection, dermatoscopy and visual examination.
The main sign indicating rosacea is persistent prolonged (at least three months) erythema of the central area of the face, which does not cover the skin area around the eyes.
Diagnostic criteria
The main ones:
-
unstable erythema;
-
persistent erythema;
-
Rosacea;
-
papules and/or pustules.
Additional:
-
burning and tingling sensation, puffiness of the face;
-
dry skin;
-
the presence of inflammatory plaques;
-
eye damage;
-
phymatous growths.
At least two criteria are required to establish a diagnosis.
Additional instrumental and laboratory studies are necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms (various dermatitis, systemic connective tissue diseases, etc.), as well as to clarify the main triggers of the disease. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the information received.
The following are used as the main diagnosis of rosacea:
-
microscopy of skin scraping
-
examination of the contents of pustules (to exclude secondary bacterial infection)
-
blood test for markers of systemic connective tissue diseases
-
Dopplerography (allows you to record changes in blood flow velocity)
Differential diagnosis
Rosacea should be differentiated from other diseases with similar symptoms: acne vulgaris, demodicosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, perioral dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, skin sarcoidosis, and chronic photodermatosis.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the accuracy of diagnosis.
Treatment of rosacea
One of the important components of effective treatment of rosacea is proper skin care and proper prevention.
-
Wash your face with warm water.
-
Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, use creams with an SPF filter of at least 30.
-
In cold weather, use greasy creams for protection.
-
Give up baths and saunas.
-
Exclude prolonged and intense physical activity.
-
Do not use creams with hormonal components, especially in the treatment of steroid rosacea.
-
Cosmetics should not contain vasodilating ingredients, alcohols, or heavy oils.
Diet is also important to ensure the success of therapy. It is recommended to exclude spicy, salty and smoked dishes from the diet, not to drink alcohol, coffee and strong tea. It is recommended to introduce more vegetables and fruits, lactic acid products into the diet. It is important to eat dishes warm, not hot.
It is necessary to find out the main source that provokes the symptoms, and exclude all circumstances that may lead to them. Observe the cause-and-effect relationships during exacerbations. This will help your doctor choose the personalized and best treatment for you.
Medical treatment of rosacea
Drug therapy is prescribed taking into account the stage, duration and features of the course of the disease, the severity of symptoms. Antibacterial therapy is prescribed in case of the infectious nature of the rash elements. In severe forms of rosacea, broad-spectrum antibiotics are often prescribed.
Nonsteroidal anti–inflammatory drugs are used to stop the inflammatory process, and in the absence of a result, glucocorticosteroids are used. Medications that reduce the activity of the sebaceous glands and normalize keratinization of the skin may be recommended.
Special creams and ointments for rosacea are prescribed for bacterial infections. They should have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, decongestant, drying and healing effects.
Antibacterial external remedies often contain metronidozole and effectively deal with most pathogens of purulent processes, eliminating pustules.
Non-drug treatment:
-
laser therapy,
-
IPL therapy (treatment with high-intensity flashes of light),
-
microcurrent therapy,
-
cryotherapy.
Laser Therapy
The principle of laser therapy (phototherapy) is the effect of a laser beam on dilated vessels, resulting in their coagulation and symptoms go away. It takes several sessions to achieve a lasting result.
Laser therapy is often part of a comprehensive rosacea treatment plan. The laser has an antiseptic and antibacterial effect, which is necessary in the treatment of papular forms of the disease. Laser therapy helps to achieve a more stable and long-lasting remission.
Cryotherapy is also one of the effective treatments for rosacea. It helps to eliminate inflammation and discomfort, restore microcirculation and metabolic processes in the skin.
Rosacea risk groups
-
Rosacea is a genetically determined disease, if relatives suffer from this disease, the person is at risk.
-
People who abuse tanning don't use sunscreens
-
People who often take contrast showers prefer hot baths
-
People who frequently change cosmetics choose the wrong daily care
-
People who often travel from hot to cold climates or are exposed to sudden temperature changes
-
People who abuse alcohol and tobacco
-
People with dry skin prone to allergic reactions
-
People with gastrointestinal disorders
Prevention of rosacea
The main prevention of rosacea is, first of all, competent vascular therapy.
Prevention of rosacea also consists in minimizing the effects of disease-provoking factors:
-
minimize exposure to the open air in strong winds and frost, use protective equipment;
-
avoid going to the solarium, do not be in direct sunlight during the period of maximum solar activity, apply cosmetics with SPF protection, wear hats with wide brims;
-
to refuse to visit the baths and saunas;
-
choose countries with a mild, cool climate to spend your holidays in;
-
maintain optimal indoor temperature and humidity;
-
minimize the presence of spicy, spicy, fatty and fried dishes in the diet, do not consume hot food and drinks;
-
eliminate alcohol and tobacco use;
-
to abandon aggressive aesthetic procedures: chemical and mechanical peels, dermabrasion;
-
provide delicate facial skin care: use mild cleansers without detergents, alcohol and other irritating ingredients, use moisturizers;
-
if the exacerbations are associated with taking medications, it is necessary to consult a doctor about their replacement.
-
avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, use creams with an SPF filter of at least 30.
-
In cold weather, use greasy creams for protection.
-
give up baths and saunas.
-
eliminate prolonged and intense physical activity.
-
do not use creams with hormonal components, especially in the treatment of steroid rosacea.
-
cosmetics should not contain vasodilating ingredients, alcohols, or heavy oils.
Rosacea is well treatable, and the course of the disease can be successfully controlled in most cases. Thanks to the professionalism of the attending dermatologist and compliance with all recommendations for treatment and prevention, it is possible to achieve stable long-term remission.
You can make an appointment with the EMC specialists by phone +7 (495) 933 66 55, or by filling out online the form on the website;
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC


.webp)
.webp)
.webp)







