Treatment of retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is a serious disease that can cause complete loss of vision in a short time.
The retina is the inner shell of the eyeball. It consists of several layers of photosensitive cells, which are the main link in the mechanism of image perception and transmission to the brain. This membrane is tightly connected to the choroid of the eye and pressed against it by the vitreous body.
If a rupture occurs in one or more areas of the retina, fluid enters the rupture from the vitreous body, ends up under the retina and peels it off. In this case, the blood supply and nutrition of the retina are disrupted, as a result of which it atrophies and dies. If urgent surgical measures are not taken at this stage, complete retinal detachment and loss of vision in the affected eye may occur.
Causes of retinal detachment
Predisposing factors of the disease include:
- high degree of myopia accompanied by "latticed" vitreochorioretinal dystrophy;
- retinal detachment in the paired eye;
- systemic diseases (Marfan syndrome, Stickler syndrome);
- proliferative diabetic retinopathy;
- history of eye injuries.
Symptoms of retinal detachment
In pathology, dark irregularly shaped spots appear in front of the eyes, dark “curtains” or gray darkening in the field of vision, “flashes", “flickers". As the disease progresses, the symptoms of retinal detachment increase, and vision in the affected eye worsens.
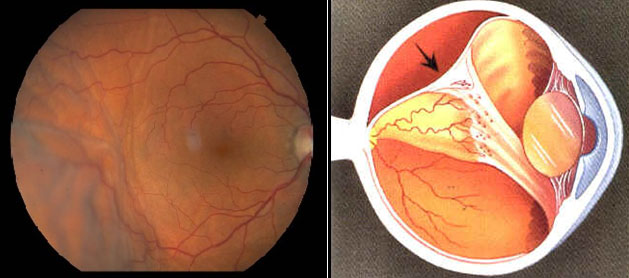
|
|
|
Retinal detachment (fundus photo)
|
Retinal detachment (diagram)
|
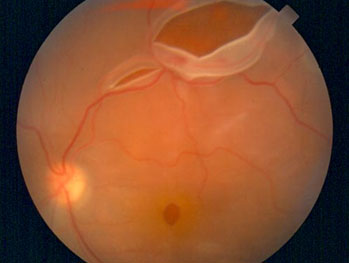
Diagnosis of retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is diagnosed by examination of the fundus. Previously, the doctor can drip drops that dilate the pupil for better visualization. Examination reveals retinal rupture, hemorrhages, and the detached retinal vesicle itself.
An ultrasound examination of the eyeball is a mandatory method of examination for suspected retinal detachment. During it, the doctor determines the prevalence of detachment, the condition of the vitreous body. Large breaks may be visualized.
Treatment of retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is treated only surgically. If the retinal detachment is small, laser or cryotherapy methods (cryopexy, cold exposure) are used. At the same time, aseptic (non-infectious) inflammation forms at the site of the rupture, subsequently causing the appearance of scar tissue tightly fusing the retina with the vascular membrane. The liquid that has penetrated under the retina gradually resolves.
If retinal detachment has occurred over a significant area, extracleral or endovitreal surgery is performed. In extracleral operations, surgical intervention is performed on the surface of the sclera (extracleral filling), which ensures a tight fit of the retina to the vascular membrane. After that, a point "welding" of the gap is performed with a laser. Endovitreal surgery involves vitrectomy - removal of the vitreous body and its replacement with an air-gas mixture or silicone oil.
The EMC clinic has a modern vitrectomy system, the CONSTELLATION Vision System from ALCON. The equipment allows for rapid seamless removal of the vitreous body through micro-punctures of the eye. At the same time, the doctor monitors the level of intraocular pressure and performs endolaser coagulation of the retina during surgery.
Laser coagulation also requires state-of-the-art equipment that ensures maximum effect with minimal risk of complications. These requirements are met by lasers installed in the EMC ophthalmology clinic: Nidek and Ellex. Retinal detachment treatment on such equipment is carried out quickly and safely, using only anesthetic drops.
In order for the postoperative period to pass as soon as possible and without complications, you should refrain from performing physical work related to weight lifting, flights, sauna visits, and follow the recommendations of your doctor.
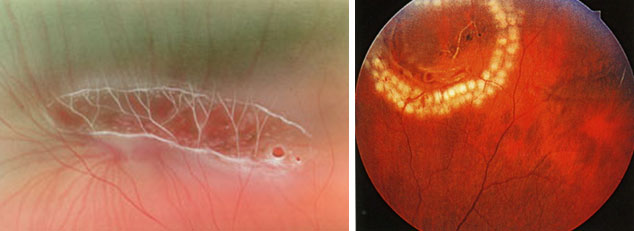
|
|
|
Retinal rupture
|
Peripheral retinal laser coagulation
|
Get help
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details.
Doctors

Elias Raid
Head of the EMC Ophthalmology Clinic, Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
-

Dmitriy Arzhukhanov
Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
-

Alfiya Bedredinova
Doctor of the highest category
-
.jpg)
Natalya Shilova
Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
-

Anna Semitko
-
.jpg)
Sergey Ignatiev
Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
-

Vitaliy Ivanov
-

Natalia Boscha
-

Oksana Levkina
Doctor of the highest category, Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
-

Viktor Makarov
Doctor of the highest category, Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
-

Elmira Sultanova
Doctor of the highest category, Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
-
Elias Raid
Head of the EMC Ophthalmology Clinic, Ph.D. of Medical Sciences
- Performs vision correction surgery
- He graduated from the MNTC "Eye Microsurgery" named after S.N.Fedorov. He has interned in various foreign clinics
- He worked in foreign clinics: Moorfields Eye Hospital,Heidelberg University Hospital,Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Bordeaux
Total experience
35 years
Experience in EMC
since 1996




