Such queries are often entered by patients in Internet search engines.
Sore throat when swallowing may be one of the symptoms of acute streptococcal tonsillitis (tonsillitis). Symptoms of angina are also general intoxication, redness of the pharyngeal mucosa, swelling of the tonsils (catarrhal sore throat), fibrinous-purulent plaque at the mouths of lacunae (lacunar sore throat), a picture of the "starry sky" (follicular sore throat), grayish-yellow plaque, which is removed to reveal superficial, slightly painful ulcers (ulcerative filmy sore throat), and regional enlargement of lymph nodes (lymphadenitis).
Angina begins with a sore throat, a sharp increase in body temperature to 39-40 ° C (sometimes up to 41 ° C) and an increase in lymph nodes. Angina can also occur with a slight increase in temperature - from 37 to 38 ° C, but with a larger area of damage to the throat.
 Sore throat can be caused by viruses and bacteria. But quite often the cause of pain is streptococcus. For example, in children over 3 years of age, about 40% of tonsillitis develops under the influence of streptococcus. Quite often, this bacterium is found in adults. The main danger of streptococcal tonsillitis is the complications it can cause. These include myocardial damage, the development of rheumatism, the formation of pharyngeal and paratonsillar abscesses, kidney damage, and even sepsis.
Sore throat can be caused by viruses and bacteria. But quite often the cause of pain is streptococcus. For example, in children over 3 years of age, about 40% of tonsillitis develops under the influence of streptococcus. Quite often, this bacterium is found in adults. The main danger of streptococcal tonsillitis is the complications it can cause. These include myocardial damage, the development of rheumatism, the formation of pharyngeal and paratonsillar abscesses, kidney damage, and even sepsis.
 EMC doctors pay great attention to the diagnosis of streptococcal infection and, at the slightest suspicion of a bacterial process, perform rapid diagnostics using modern test systems.
EMC doctors pay great attention to the diagnosis of streptococcal infection and, at the slightest suspicion of a bacterial process, perform rapid diagnostics using modern test systems.
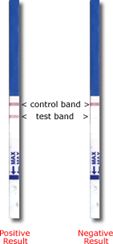
The procedure is quite simple and takes about 5 minutes, the test itself is somewhat similar to a pregnancy test, and the material is a smear from the tonsils. One strip is a negative test, two strips are positive. In case of a positive result, the doctor immediately prescribes specific antibacterial therapy.







.webp)


.webp)

.webp)

.webp)




.webp)


.webp)

.webp)
