Children's high activity and carelessness often cause injuries and dental damage. It is often the front teeth that are injured.
Acute injuries to teeth, jaw or surrounding tissues in children: signs
-
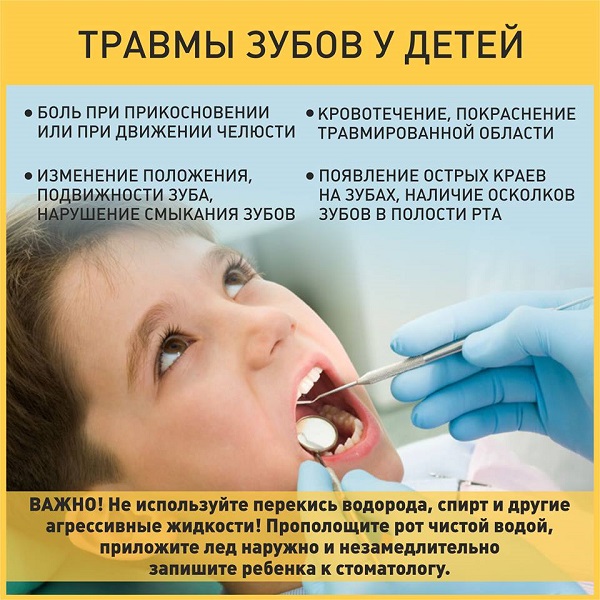
Pain when touching or moving the jaw, spontaneous pain.
-
Bleeding, redness of the injured area.
-
Tooth position change, tooth mobility, tooth closure disorder.
-
The appearance of sharp edges on the teeth, the presence of fragments of teeth in the oral cavity.
If a child has a baby tooth or soft tissue injury:
-
Don't panic and try to calm the child down.
-
Perform an examination for damage to soft tissues (lips, cheeks, tongue).
-
Do not attempt to set a dislocated tooth or a tooth fragment.
-
Wipe the child's face, rinse (rinse) the mouth with water.
-
Apply ice externally for 5-10 minutes to stop bleeding, reduce swelling and pain. If the bleeding continues, repeat the procedure every 5 minutes.
-
Try to find the dislodged tooth (fragments), rinse it carefully (without using brushes, special detergents and solutions) under running water.
-
Place the tooth (fragment) in a container with milk or salted water.
IMPORTANT! Do not use hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, or other aggressive liquids.
In case of damage, the child should be immediately enrolled in a consultation with a pediatric dentist. The success of treatment depends on the timeliness of treatment!
Depending on the nature of the injury, the doctor will determine the need for surgical or therapeutic treatment. Modern technologies in most cases make it possible to save a damaged tooth, which is especially important in case of permanent teeth injuries. Many parents prefer to remove a baby's injured baby tooth, but its premature removal can negatively affect the health of permanent teeth and bite formation.
Diagnostics
A number of examinations are conducted to identify the nature of the injury. At the consultation, the dentist determines the degree of damage to the tooth and surrounding tissues, identifies possible displacement, tooth staining, occlusion disorder, etc.
Instrumental examinations can clarify the nature of the injury: electrodontometric measurements, transillumination method and radiography.
Even if only one tooth is injured, it is necessary to perform percussion (tapping) of adjacent teeth to avoid damage to them. Vertical percussion reveals the degree of damage to the periapical tissues, while horizontal percussion diagnoses swelling or hemorrhage in the pulp.
An X-ray is required. It provides complete information about the injured tooth: the direction of dislocation, the condition of the equine system, the presence of tooth gouging and periapical changes. According to the X-ray, the dentist evaluates the periodontal condition, the width of the pulp chamber, and the germ zone.
The Children's Clinic fully provides highly qualified assistance using modern diagnostic methods (cone beam computed tomography, orthopantomogram, targeted visiography) and safe anesthetics. The Children's clinic provides a full range of dental care, if necessary, with the involvement of specialized specialists, not only on an outpatient basis, but also in the hospital.
If necessary, all manipulations are performed under medical sleep conditions.
Accurate, timely diagnosis and effective treatment will allow your baby to keep the tooth. And prevention and regular professional oral care will help them stay healthy.
Prevention of dental injuries
In most cases, children get dental injuries during sports or outdoor games. The use of personal protective equipment, such as a helmet with chin protection or individual mouth guards, will help reduce the risk of injury.












.webp)





.webp)






