Pharyngitis in children: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Narrated by Zinaida Bogolepova,
otorhinolaryngologist, phoniatrist
 Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa. It is rarely an independent disease (especially in children), it occurs more often against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, influenza, Epstein-Barr virus, etc. Pharyngitis can also be caused by a bacterial infection.
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa. It is rarely an independent disease (especially in children), it occurs more often against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, influenza, Epstein-Barr virus, etc. Pharyngitis can also be caused by a bacterial infection.
Factors contributing to the development of pharyngitis:
- hypothermia;
- spicy, very cold food (ice cream);
- mouth breathing (especially in winter);
- decreased immunity;
- exposure to exogenous factors (gas pollution, dustiness of the air, tobacco smoke);
- vitamin deficiency;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, etc.);
- allergy.
Classification of pharyngitis:
Acute, subacute, and chronic.
According to the condition of the pharyngeal mucosa:
- catarrhal — edema, redness of the mucous membrane of the throat, larynx, gradually the mucous membrane becomes grayish-pink. hypertrophic — thickening of the mucous membrane of the larynx and throat due to the proliferation of epithelial tissue. Hypertrophy of the lateral pharyngeal ridges, thickening of the palatine arches, and the appearance of nodules and granules on the posterior pharyngeal wall usually occur.
- subfatrophic — thinning of the tissues of the throat and larynx of a focal or diffuse nature. Externally, the mucous membrane is pale, dry, and the vessels are thinned and atrophied.
The main symptoms of pharyngitis:
- sore throat, coughing, dry mouth;
- difficulty and pain when swallowing;
- feeling of scratching, sore throat;
- dry cough;
- with inflammation of the vocal folds, hoarseness and a change in the timbre of the voice appear;
- in young children, it may be accompanied by fever, refusal to eat, physical inactivity, sleep disorders, and nausea; a feeling of bitterness and sourness in the mouth (if there is a reflux nature of the disease).
When the tonsils are involved in the process, angina may develop, in which case plaque most often appears on the tonsils.
Sore throat with pharyngitis is moderate, appears only when swallowing food, especially hot or hard. With angina, the pain in the throat is constant, intense, and increases when swallowing or taking fluids.
When the tonsils are affected, the temperature rises quickly and sometimes up to 40 degrees, often a white plaque appears the next day. And pharyngitis usually begins with a sore throat, and after that, or at the same time, the temperature rises slightly.
If the child is small and cannot tell what is bothering him, the body temperature rises to 39 °, you should immediately contact a pediatrician. If treatment at home for two days does not improve your well-being, you should also consult a doctor. Parents often prescribe medications themselves, and buy alcohol-based concentrated solutions that only dry out the mucous membrane. And by the time the patient comes to the clinic, in addition to the treatment of pharyngitis, it is also necessary to restore the mucous membrane. Moreover, dryness of the mucous membrane prolongs the course of the disease.
You should not get carried away with self-medication, it is important to remember that only a doctor after a thorough diagnosis can prescribe a drug taking into account all the individual characteristics of a child.
If pharyngitis recurs or does not go away for a long time, this is a reason to look for the true causes of the disease, moreover, pharyngitis is rarely an independent disease and often accompanies adenoiditis, tonsillitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Diagnosis of pharyngitis
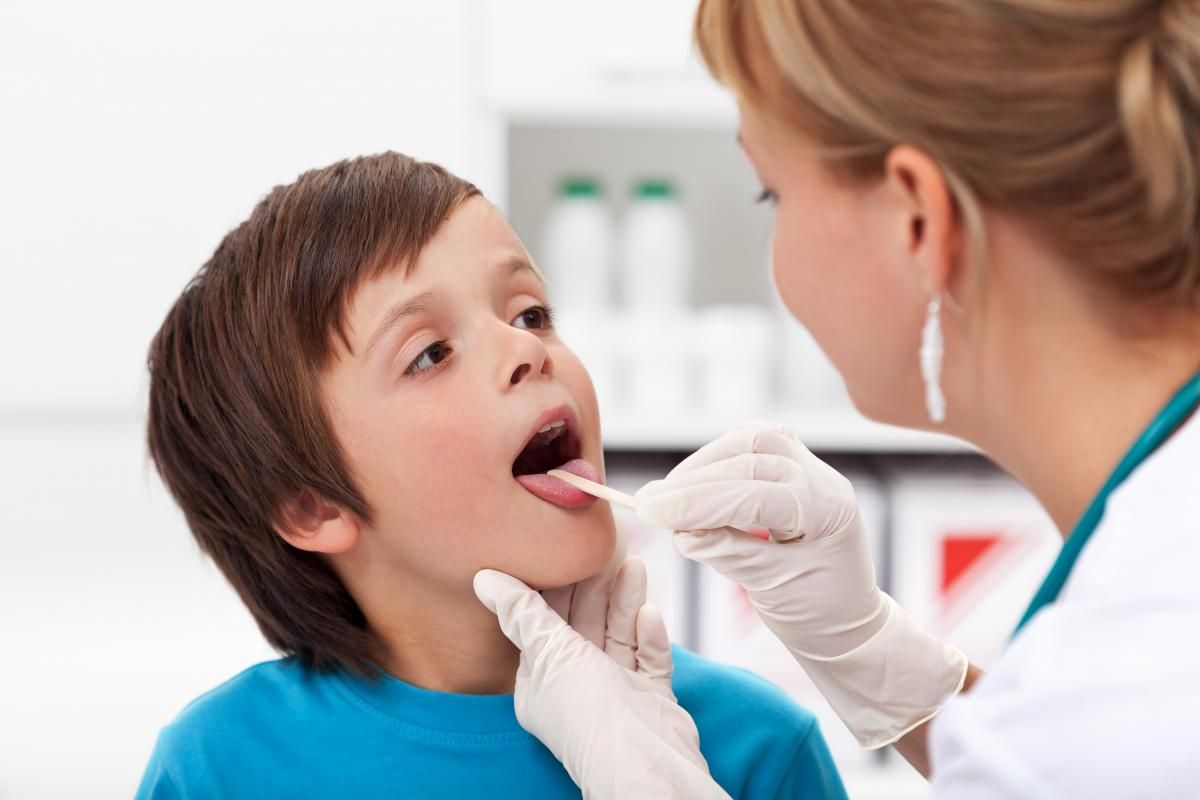
The first specialist that parents turn to is a pediatrician. If the disease returns, if not all the symptoms go away after treatment, an otorhinolaryngologist is involved in the process. It is very important to understand the causes, because many diseases are disguised as acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections. For example, there are situations when, without a properly established diagnosis, treatment, and special vocal regimen, a child with pharyngolaryngitis strains the vocal cords during the day, which provokes the development of vocal fold nodules, which in turn require longer and more complex treatment, and sometimes surgical.
Laboratory tests:
- pharyngeal swab for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics or PCR;
- general blood test.
With recurrent pharyngitis:
- endoscopy of the nose and nasopharynx;
- allergist's examination (to exclude the allergic nature of the disease);
- examination by a gastroenterologist (to rule out reflux disease);
- Endoscopy (fibroscopy) of the larynx (for pharyngitis).
Treatment of pharyngitis in children
- It is necessary to exclude from the diet all irritating mucous foods (too hot and cold, salty, sour, spicy). The patient is recommended to drink plenty of water (up to two liters per day).
- Gargling is prescribed for children starting from the age of 3.
- It is recommended to consume liquid dishes that do not cause difficulty in swallowing (chicken broths, soups, porridges, fruit and vegetable mixtures).
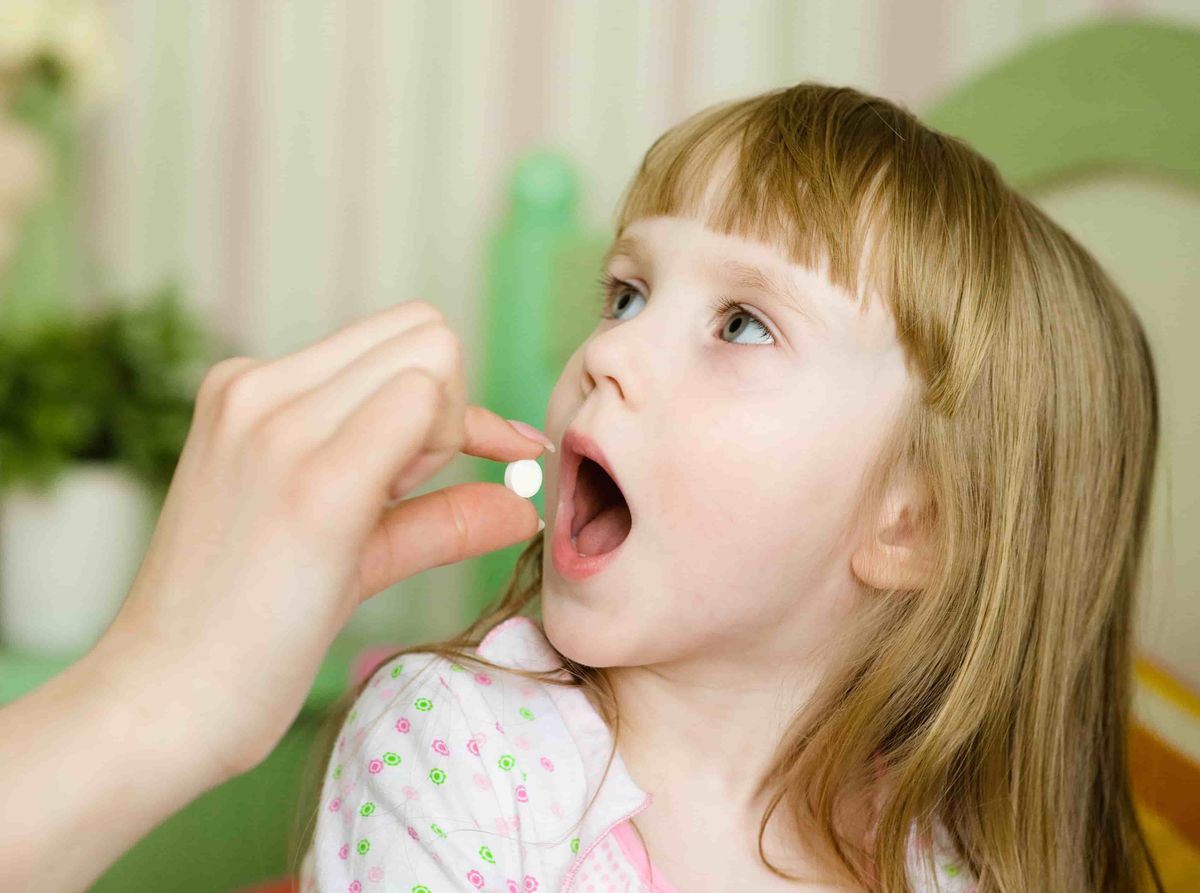 Antiseptics. They are prescribed depending on the nature of the course of the disease and the condition of the mucous membrane.
Antiseptics. They are prescribed depending on the nature of the course of the disease and the condition of the mucous membrane.
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed from the first day if group A hemolytic streptococcus is detected. In other cases, it all depends on the severity of the disease and the results of laboratory tests.
Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce body temperature.
With pharyngolaryngitis, they are shown:
Voice mode (voice rest). Limit communication, especially on the phone, do not whisper, do not sing, do not shout, it is best not to talk.
Alkaline drink.
Inhalations. For children, it is better to choose ultrasonic or compressor inhalers. If the child has a history of laryngospasm (false croup), an inhaler must be provided so that parents can independently inhale the topical hormone in critical situations before the ambulance arrives.
Humidification of indoor air. Dryness of the air can prolong the course of the disease.
Antihistamines to relieve edema.
The EMC Children's Clinic has all the facilities for the treatment of pharyngitis and pharyngolaryngitis. Doctors of all children's specializations receive appointments in one building, examinations are carried out around the clock, and emergency and emergency doctors are ready to visit young patients at any time. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out as soon as possible. Within the framework of a multidisciplinary approach, doctors of various specialties (pediatrician, otorhinolaryngologist, allergist, gastroenterologist, etc.) take part in the treatment of patients, the decision in difficult cases is made by a council of doctors.
Author: Zinaida Bogolepova, otorhinolaryngologist, phoniatrist
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC







.webp)





.webp)






