Glioblastoma of the brain
If left untreated, a sick person dies within a few months of the onset of the first symptoms. However, timely treatment can significantly increase the patient's life expectancy. In evidence-based medicine, there are observations when, after high-quality therapy, the patient's life lasts for many years.
With this method of treatment, the drug is selected based on molecular genetic tests, which allows for the most effective treatment for a particular case. In addition, this method allows you to act exclusively on the affected cells and not damage healthy ones.
In the course of targeted therapy, the use of Bevacizumab or Avastin has a particularly positive effect. The drug is administered through a venous catheter. It strikes the blood vessels that are involved in the formation of glioblastoma. As a result, the malignant cells are destroyed. Bevacizumab is most often used to control relapses.Advantages of targeted therapy in EMC
EMC is the only clinic that provides the most comprehensive genomic profiling service for the selection of targeted therapies. This method is also used in the fight against glioblastoma. EMC specialists compile a molecular genetic portrait of the tumor without obtaining a sample of its tissue: the patient's blood plasma is sufficient.
Causes of occurrence
Glioblastoma is a malignant tumor that forms most often in the brain, but it can also rarely begin to develop in the spinal cord.
Recent scientific evidence shows that glioblastoma develops from astrocytic glial cells of the brain (auxiliary cells of the nervous tissue) or their precursors, including stem neutral cells responsible for the constant renewal of nervous tissue. Combinations of mutations can occur in these cells that disrupt the mechanisms of cell division and interaction, leading to the appearance of aggressive tumor clones. The appearance of these mutations is usually spontaneous and has no proven association with most external factors, such as smoking, exposure to electromagnetic fields, head injury, or dietary preferences.
However, scientific evidence shows that the risk of glioblastoma increases when exposed to ionizing radiation.
There are a number of genetic syndromes in which the risk of additional abnormalities in the DNA structure of glial cells leading to the development of glioblastoma is increased. For example, these risks increase when a person has type I neurofibromatosis and Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
With age, the risk of developing a brain tumor increases. This happens because a person's DNA protection mechanisms against mutations decrease, and the effectiveness of the immune system decreases.
Only a competent and timely combination of modern treatments can give a patient a chance to significantly prolong life and improve its quality. In some cases, it is possible to achieve a significant prolongation of life from the moment of glioblastoma diagnosis.
Advantages of EMC glioblastoma treatment



Glioblastoma surgery
According to current international standards, the treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma, in most cases, begins with surgery.
It is necessary to remove the bulk of malignant cells from the brain, eliminate compression of the surrounding healthy nervous tissue, and reduce cerebral edema. In addition, during surgery, the tumor tissue is sent for histological and molecular genetic studies, which are extremely important for making a correct final diagnosis and prescribing adequate follow-up treatment. In some cases, part of the removed pathological tissue can be used to create personalized immunotherapy (for example, activated lymphocytes or dendritic cells)
.
After glioblastoma removal surgery, according to international standards, all patients undergo a control MRI of the brain with contrast in order to accurately determine the degree of tumor removal and confirm the absence of any complications in the surgical area.
After the pathologist confirms the diagnosis of glioblastoma based on the results of histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic studies, a multidisciplinary consultation is conducted at the clinic, which involves neurosurgeons, radiologists, oncologists, neuroimaging specialists, and pathologists. This council approves further treatment tactics based on international standards, taking into account the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
In the EMC clinic, operations to remove glioblastoma of the brain are performed by highly professional neurosurgeons. Specialists have the most modern technologies at their disposal to achieve the most complete removal of the tumor with minimal risk of damage to the surrounding functionally significant normal brain tissue.
For this purpose, EMS uses intraoperative MRI, metabolic navigation based on 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA), and intraoperative neuromonitoring.
Radiation therapy
Surgical intervention for glioblastoma, no matter how well it was performed, unfortunately, is not healing. This is due to the fact that microscopic structures invade the surrounding brain tissue.
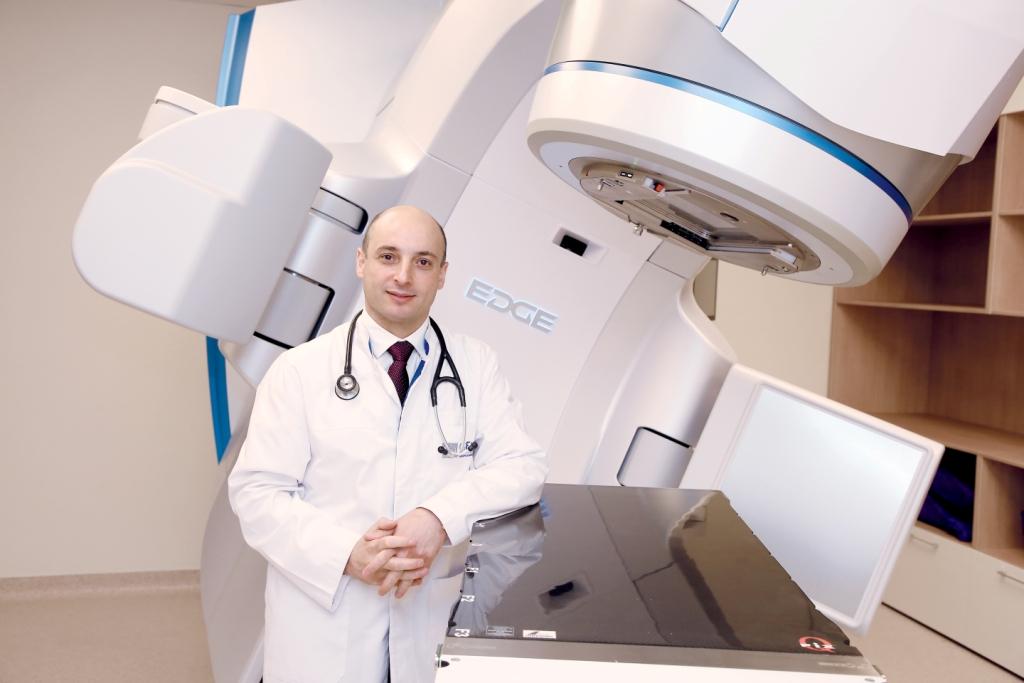 In order to suppress the residual tumor tissue, the patient requires continued treatment by oncologists, radiologists and chemotherapists, which must begin within 1 month after the operation. Chemoradiotherapy is performed for 6 weeks. During this time period, the patient receives radiation therapy sessions every 5 days a week.
In order to suppress the residual tumor tissue, the patient requires continued treatment by oncologists, radiologists and chemotherapists, which must begin within 1 month after the operation. Chemoradiotherapy is performed for 6 weeks. During this time period, the patient receives radiation therapy sessions every 5 days a week.
Oncologists and radiologists irradiate the cavity remaining after the removal of the bulk of the tumor, its walls, with the capture of the surrounding post-resection cavity of the brain tissue.
At the same time, without interruptions, the patient receives daily treatment with temozolomide, the dose of which is calculated by oncologists individually for each case.
The EMC Institute of Oncology has introduced a unique technique of intraoperative Xoft radiation therapy for recurrent gliomas, which significantly prolongs the life of patients.
At the EMC clinic, radiation therapy is performed using state-of-the-art Varian EDGE equipment, which increases the effectiveness of treatment and minimizes negative consequences for the patient.
For the first time in international neuro-oncology, the EMC specialists used intraoperative balloon electronic brachytherapy, implemented on Axxent Xoft equipment, to treat recurrent and progressive glioblastomas. This method allows during surgery, immediately after removal of the main mass of the malignant tumor, to irradiate the surrounding brain tissue over the entire area containing residual microscopic elements of the tumor, preventing them from activating early after surgery. At the same time, excessive irradiation of important surrounding structures of the brain can be avoided.
Chemotherapy
The third stage of glioblastoma treatment consists of 6 consecutive monthly cycles of Temozolomide chemotherapy, conducted under the supervision of a chemotherapist.
In glioblastoma, Temozolomide prolongs the disease-free period and the overall life expectancy of the patient.
Targeted therapy
Improving the quality of life of patients with recurrent glioblastoma can be achieved by prescribing the targeted drug bevacizumab, which is a blocker of vascular endothelial growth factor and reduces the patient's need for dexamethasone.
The targeted drug attacks the blood vessels that are involved in the formation of glioblastoma.
Symptoms of glioblastoma
The symptoms of the disease accompanying the patient depend on the size and type of tumor. Common symptoms include persistent headaches, epileptic seizures, problems with coordination, speech and visual clarity, seizures, increased irritability, nausea, vomiting, and confusion. These symptoms are common to other diseases, so it is important to perform a detailed diagnosis in order to accurately determine the diagnosis.Diagnosis of cerebral glioblastoma
Diagnosis is necessary not only for patients who have applied to the EMC Institute of Oncology for the first time, but also for those who have already undergone treatment and are monitoring its effectiveness. During the first 3 years after chemoradiotherapy, the patient should be closely monitored by an oncologist specializing in neuro-oncology, since during this time (especially the first 6-9 months) the risks of recurrence or progression of the disease are highest.
MRI with contrast
For adequate disease control, it is important to perform an MRI scan of the brain with contrast every 2-4 months (it is highly desirable to supplement this study with MR perfusion) and come for a follow-up examination to an oncologist who conducts a general examination and evaluates the results of the MRI.
A special feature of our approach is performing an MRI scan of the brain with contrast enhancement and perfusion on the first day after surgery to assess the success of surgical treatment. In the future, this MRI will serve as a model for spot radiation therapy to the area of interest and to prevent recurrence.
PET-CT
If the results of the control MRI examination do not allow us to judge with certainty the absence or presence of glioblastoma progression, the patient is prescribed a PET-CT scan of the brain with an amino acid-based radiopharmaceutical.
The EMC Clinic is a leader in PET technology in Moscow and uses 18F-fluoroethylthyrosine (18F-FET) for this purpose, which has proven its advantage in numerous studies, allowing it to detect tumor progression in complex diagnostic cases, allowing timely and adequate response to the current situation, up to the need for repeated neurosurgical intervention.
The cost of brain glioblastoma treatment at the European Medical Center is calculated individually after consulting an oncologist.
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC






.webp)

