Treatment of angina in a child
We are all surrounded by microorganisms every minute, including many pathogenic bacteria, viruses and fungi. When the number of such microorganisms becomes too large, angina can develop against the background of weakened immunity.
Chronic diseases of the ENT organs and caries are also risk factors.
Classification of angina
Angina in children is divided into 2 types: acute and chronic.
Acute angina develops from 2 to 4 days, while the general symptoms are vivid – sore throat, fever, changes in the condition of the tonsils, enlarged lymph nodes. With an exacerbation of chronic angina, there are no vivid manifestations. This process is often confused with a common viral infection.
Angina in children is divided according to the type of plaque and changes on the tonsils: catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, fibrinous, phlegmonous (intratonsillar abscess), ulcerative necrotic or gangrenous.
According to the type of pathogens: herpes, fungal, viral, bacterial, mixed.
Symptoms of angina
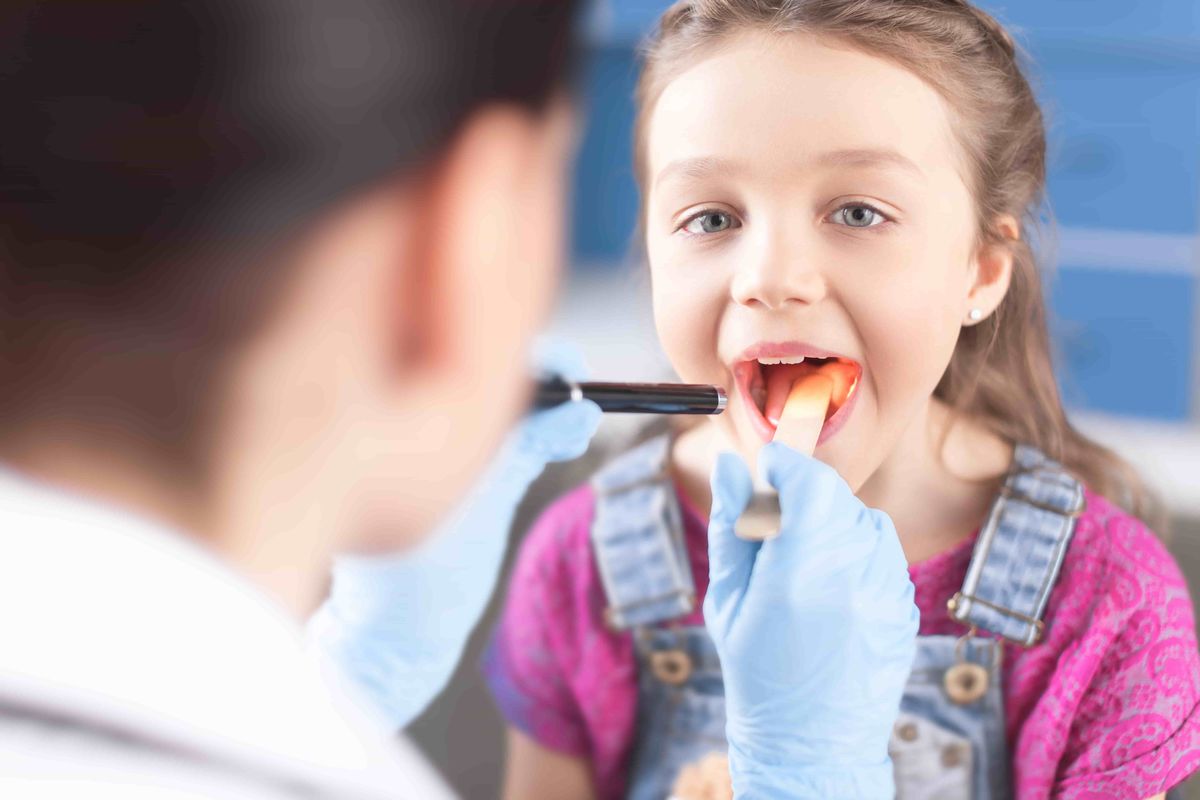 Signs of inflammation: sore throat, including when swallowing, changes in the condition of the tonsils (redness, plaque, blisters, ulceration), an increase in body temperature to 38⁰ and above. Additional signs of the disease may include inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck and submandibular region, pain and limited movement in the cervical spine. Children often complain of general ill health, headache, nausea, and refuse to eat or drink. A particularly dangerous symptom is signs of respiratory distress due to excessive swelling of the tonsils or palatine arches.
Signs of inflammation: sore throat, including when swallowing, changes in the condition of the tonsils (redness, plaque, blisters, ulceration), an increase in body temperature to 38⁰ and above. Additional signs of the disease may include inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck and submandibular region, pain and limited movement in the cervical spine. Children often complain of general ill health, headache, nausea, and refuse to eat or drink. A particularly dangerous symptom is signs of respiratory distress due to excessive swelling of the tonsils or palatine arches.
Complications of angina
The most common complications occur with phlegmonous sore throat, when bacteria release toxins that can melt the tonsil tissue to form a purulent abscess. Treatment of purulent sore throat in children should be started immediately, before the abscess is opened, since its development manifests itself not only in a toxic effect, but may be accompanied by impaired swallowing and / or breathing of the child. And an independent breakthrough of the abscess into the surrounding tissues will lead to the formation of purulent congestion.
Raids that are not removed by a doctor in time with ulcerative necrotic sore throat can lead to the seizure of the entire amygdala by the pathological process and go beyond its limits. In such cases, surgical treatment is inevitable.
The most dangerous complication is the development of rheumatic lesions, when anti-streptococcal antibodies, forming an aggressive immune complex, can become fixed in the tissues of the heart valves and/or on the articular surfaces, leading to their destruction. That is why it is so important to make sure that 3 months after the date of recovery, the described immune complexes in the form of Antistreptolysin (ASLO) do not circulate in the blood. If they are detected, additional laboratory tests and preventive antirheumatic measures should be performed.
Diagnosis of angina
To diagnose angina in the EMC Children's Clinic, a smear is taken for pathogenic streptococcus (Streptest) and a group of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. Streptest is an express diagnostic method, its results become known after 15 minutes.
The nature of the disease (bacterial, viral) is determined by clinical blood analysis and analysis for C-reactive protein (CRP). The studies are conducted in the clinic, and the attending physician receives the result in 20 minutes.
Angina in children: treatment
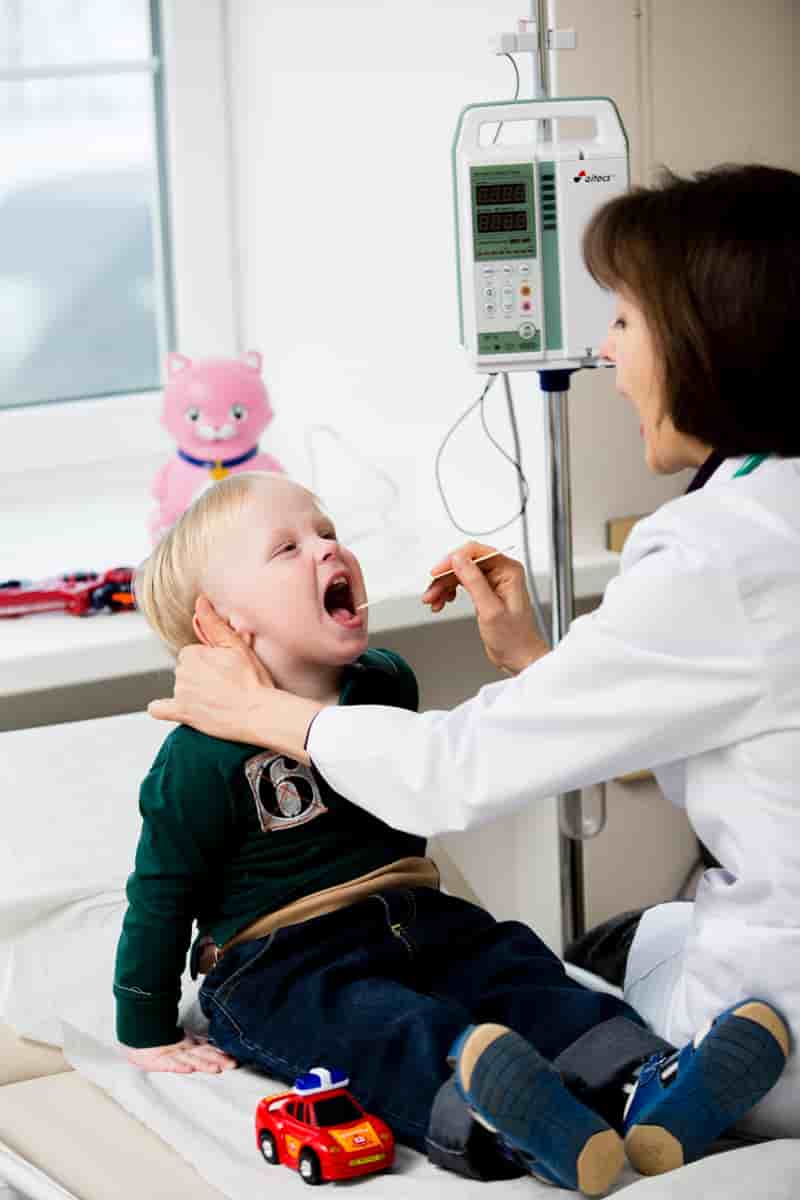 The EMC Children's Clinic treats angina both on an outpatient basis and in a comfortable hospital.
The EMC Children's Clinic treats angina both on an outpatient basis and in a comfortable hospital.
If there is no need for surgical treatment, treatment of sore throats (including treatment of herpes sore throat) in children is carried out with drugs that are selected individually, taking into account tolerance, the state of the gastrointestinal tract, an allergic history, and also taking into account the causative agent of the disease.
In addition to antimicrobial (antiviral, antifungal) drugs, painkillers, antipyretics and antiallergic drugs are prescribed.
Treatment of angina in the Children's Clinic is carried out by highly qualified pediatricians.
Modern medicine does not welcome local treatment of sore throats with rinsing, when the already inflamed arches strain excessively, and pathogens can be carried beyond the locus of inflammation, leading to the spread of the process.
The advantage is given to such local treatment methods as irrigation or drug treatment of the tonsils and/or palatine arches.
And remember – no warming procedures, hot water bottles and compresses. It can only harm the child!
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC







.webp)





.webp)






