Polyps of the colon
Tells Elmurat Lafishev - coloproctologist, surgeon
What is a "polyp"?
 Polyps are growths of the inner layer of the colon wall that protrude into the intestinal lumen. There are two types of polyps in shape: on the stem (they are usually small, with a smooth surface, resemble a mushroom) and on a wide base (flatter and larger, creeping, soft, "villous"), their sizes can vary from a few millimeters to centimeters. Polyps, as a rule, do not bother the patient until a certain time and are accidentally detected during endoscopic (colonoscopy /rectosigmoscopy) or X-ray (irrigoscopy) examination of the intestine. In some cases, large polyps can cause discomfort, pain in the anus and abdomen, stool disorders, which may also be signs of other diseases (hemorrhoids, anal fissure, inflammatory bowel diseases, and others). In cases where the polyp is located in the lower intestine (rectum or sigmoid colon), the polyps may appear as a strip of blood and/or mucus on the surface of the stool.
Polyps are growths of the inner layer of the colon wall that protrude into the intestinal lumen. There are two types of polyps in shape: on the stem (they are usually small, with a smooth surface, resemble a mushroom) and on a wide base (flatter and larger, creeping, soft, "villous"), their sizes can vary from a few millimeters to centimeters. Polyps, as a rule, do not bother the patient until a certain time and are accidentally detected during endoscopic (colonoscopy /rectosigmoscopy) or X-ray (irrigoscopy) examination of the intestine. In some cases, large polyps can cause discomfort, pain in the anus and abdomen, stool disorders, which may also be signs of other diseases (hemorrhoids, anal fissure, inflammatory bowel diseases, and others). In cases where the polyp is located in the lower intestine (rectum or sigmoid colon), the polyps may appear as a strip of blood and/or mucus on the surface of the stool.
Inflammatory polyps are distinguished (they appear at the site of inflammation), hyperplastic (the result of excessive overgrowth of normal tissue) and neoplastic (with the presence of atypical cells).Most polyps are benign formations, but in some cases they can degenerate into cancer. This transformation is more typical for villous glandular polyps.
How are colon polyps diagnosed?
The main method of diagnosing polyps is colonoscopy. This endoscopic (intraluminal) examination allows you to visually assess the condition of the colon along almost its entire length (about 2 meters) and, if polyps are detected, remove them during the procedure and/or perform a biopsy. In EMC, colonoscopy is performed using short-term sedation (anesthesia), which avoids the unpleasant sensations associated with inserting a probe (endoscope) and pumping air to straighten the intestine.
There are alternative methods for diagnosing colon polyps, but each of them has its limitations. For example, rectosigmoscopy allows you to examine only the rectum and lower colon, while the probability of detecting polyps in other parts of the intestine is high.Irrigoscopy (X—ray examination of the colon using a contrast agent - barium suspension) allows you to detect a polyp, but it provides very approximate information about its structure and does not allow you to take a tissue sample for examination. Therefore, if polyps are detected by any of these methods, the patient is necessarily referred for a colonoscopy.
Why are polyps considered a precancerous disease?
Not all polyps degenerate into cancer, however, it is believed that in 80% of cases colon cancer is preceded by the stage of a benign polyp. Therefore, the polyp is considered as a precancerous disease, involving its endoscopic removal (polypectomy) in order to prevent the development of a malignant tumor.
What should I do if polyps are found in the colon?
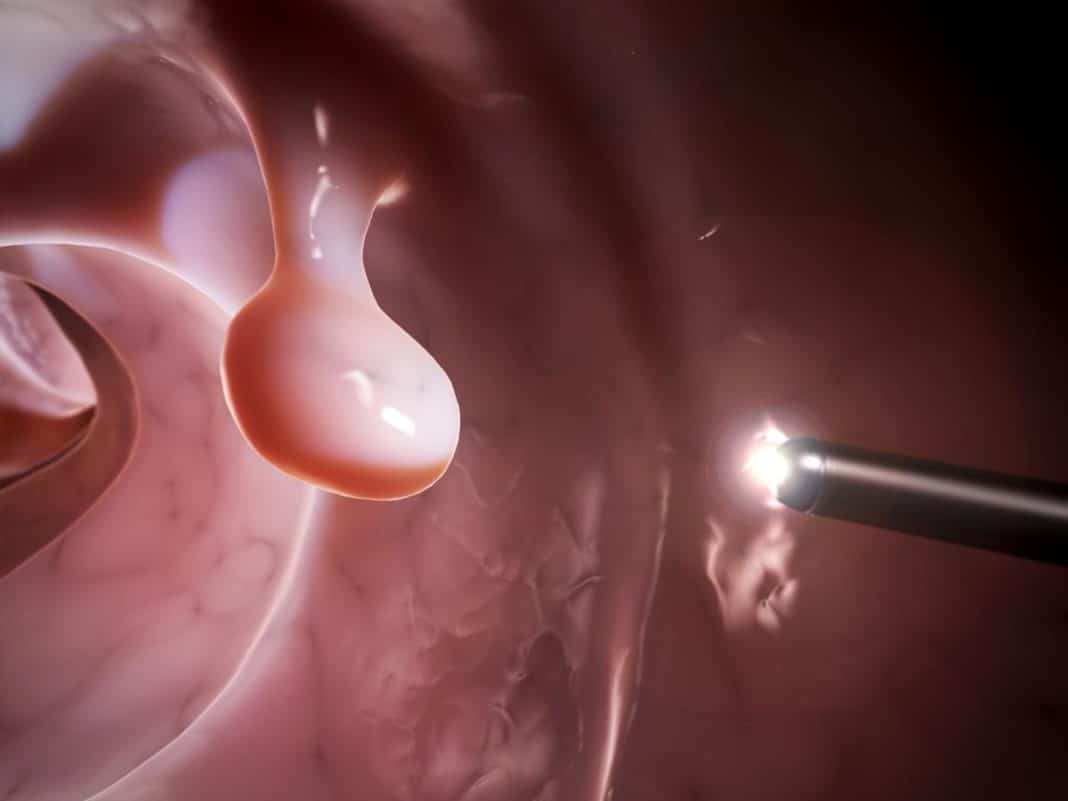 Traditionally, any polyp found during colonoscopy should be removed and sent for histological examination. There are no medical treatments for colon polyps. There are only assumptions about reducing the risk of developing polyps when taking certain medications.
Traditionally, any polyp found during colonoscopy should be removed and sent for histological examination. There are no medical treatments for colon polyps. There are only assumptions about reducing the risk of developing polyps when taking certain medications.
Removal of colon polyps (polypectomy) in most cases is carried out using endoscopic equipment — using a special instrument at the end of which there is an electrode in the form of a loop.
Sometimes, several procedures may be required to remove large polyps. If the size and location of the polyps do not allow this manipulation endoscopically, surgical intervention is required – resection of a part of the intestine with a tumor.
What is a "biopsy"?
A biopsy is the collection of tissue samples of the colon mucosa for histological examination. It is not always possible to remove a polyp during colonoscopy, for example, if it is a villous polyp on a wide base, easily injured and bleeding. Then the doctor pinches off a piece of the pathological formation found during colonoscopy and sends it to the laboratory for examination under a microscope. This allows you to quickly and accurately diagnose, including at the earliest stages of the disease. Based on the histological examination data, the doctor chooses the best treatment strategy in each clinical case.
Glasses with tissue samples are usually stored for possible subsequent examination of the micropreparation in another medical institution.
Can polyps recur?
After the polyp is removed, the possibility of its recurrence is minimal. However, the factors that cause the formation of polyps have not been eliminated, so in some patients, polyps may form again. Patients who have ever had colon polyps should continue to undergo regular examination by a coloproctologist. The frequency of colonoscopy is determined individually in each case, taking into account the patient's risk factors for the degeneration of polyps into cancer. After removal of large polyps (more than 2 cm), multiple (5 or more) and villous polyps of any size, colonoscopy is necessary every year. In addition, we recommend that all patients over the age of 50 have a colonoscopy as part of colorectal cancer screening, since statistics show that starting at this age, the risk of developing this type of cancer increases significantly. In the future, screening studies should be repeated in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician.
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC
.webp)







.webp)

.webp)
.webp)





.webp)


