Sometimes multiple IVF attempts with oocytes that are good from the point of view of embryology fail: for example, an implanted embryo does not take root and dies.
Why can this happen? The morphology of the oocyte division spindle is of great importance.
The structure of the egg, and what is the spindle of division?
The quality of the embryo and its development potential depend on the quality of the oocyte. The shape of the cell, the structure of the cytoplasm, the shell and the polar body (the cell separating from the oocyte during maturation) are usually evaluated. The egg itself may have an abnormal shape – oval or amorphous. The cytoplasm may have vacuoles (cavities inside the cell filled with cell juice), various inclusions, and an abnormal shape. The oocyte shell can be thick, thin, or carry any abnormalities: the polar body may be absent, fragmented, or located separately from the cell itself. All these anomalies affect the further development of the embryo to varying degrees.
There is another very important element in the oocyte – the spindle of division (Fig.1).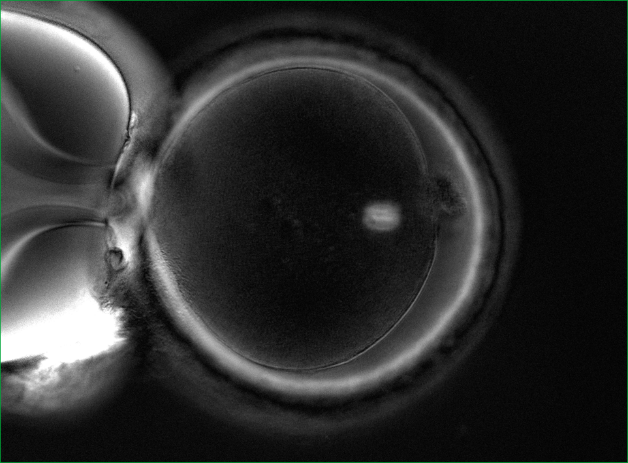
Who is shown the procedure for evaluating the division spindle?
1. For patients aged 40+. It is a well-known fact that with age, the percentage of oocytes with problems with chromosome separation increases. These problems lead to genetic mutations.
2. Patients with a large number of oocytes and poor embryo development (in particular, polycystic ovary syndrome).
3. Patients who have had multiple IVF attempts with good eggs from the point of view of embryology, but with embryos that do not take root after transplantation, or with early pregnancy losses.
How can the division spindle be evaluated?
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2).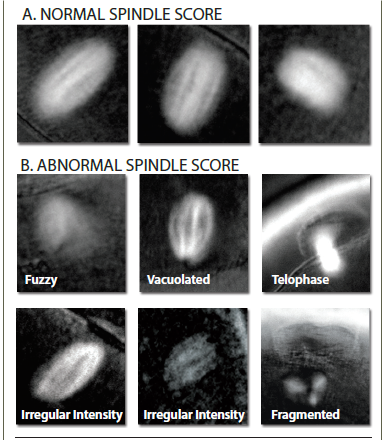 If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).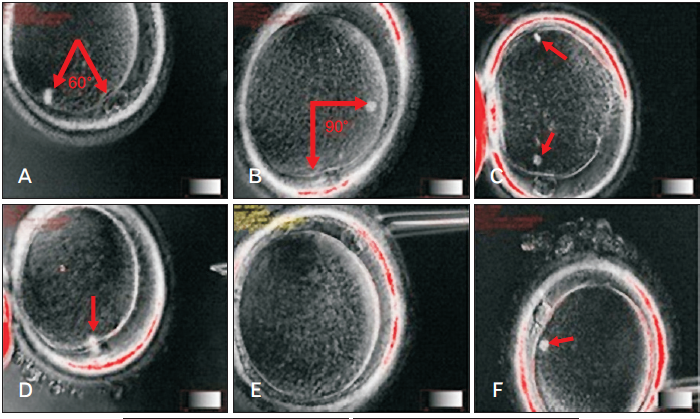 And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.

Who is shown the procedure for evaluating the division spindle?
1. For patients aged 40+. It is a well-known fact that with age, the percentage of oocytes with problems with chromosome separation increases. These problems lead to genetic mutations.
2. Patients with a large number of oocytes and poor embryo development (in particular, polycystic ovary syndrome).
3. Patients who have had multiple IVF attempts with good eggs from the point of view of embryology, but with embryos that do not take root after transplantation, or with early pregnancy losses.
How can the division spindle be evaluated?
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2). If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3). And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2). If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3). And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.

 And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.
Was this information helpful?
Questions and answers
Рancreatic cancer
My wife of 64 years was diagnosed with pancreatic cancer in the autumn of 2014. Stage 4 was concluded. Surgery is impossible. There is a massive thrombosis. Three biopsies were carried out. A benign tumor was revealed. She lost a lot of weight. An episode of severe pain took place about one month ago. Currently, a
significant problem is the ascites, swollen legs; food is poorly digested, general discomfort. What can you recommend? Is it necessary to remove the fluid and what might be the consequences?
...more The picture you described is consisted with the concept of "metastatic ascites". Laparocentesis is appropriate as a therapeutic and diagnostic approach. Given the negative cytology, it is likely that the patient has a neoplastic disease of the colon, ovaries or stomach. Our experts will hold a consultation on the
same day and perform the procedure to verify the diagnosis and consider the possibilities of palliative treatment.
...more 
Pavel Koposov
07 September 2016
Break iafter the last course of chemotherapy
Why a break is necessary after the last course of chemotherapy?
In cases where chemotherapy is not enough effective, some cells of the tumor does not die as a result of exposure and only slow down their biological processes temporarily, so they do not accumulate diagnostic radiopharmaceutical that can lead to a false negative result. After 2-3 weeks, tumor cells return to their
normal state and can be seen at the PET/CT scan. Thus, the break after the last course of chemotherapy should be done in order to obtain reliable results of the quality of treatment.
...more
Radiation therapy for prostate cancer
What to expect during radiation therapy for prostate cancer?
The procedure of external radiotherapy is similar to conventional x-ray examination. Radiation is invisible, has no smell and gives no sensations, side effects do not appear until 2nd or 3rd week of treatment.
Radiotherapy for prostate cancer is a local treatment; therefore, you may experience some side effects
only in those parts of the body that are exposed.
...more
Сhronic nonspecific spondylitis
Can we go to your center in the following case: the patient born in 1955. Diagnosis: chronic nonspecific spondylitis T7-T9. A state after interbody fusion T7-T9 with autologous bone. Brown-Sequard's syndrome. Right thoracotomy with interbody fusion using autotransplantation (resected rib) was done in 2010, no bone
block formed during the postoperative period. Transpedicular fixation T 5-6-10-11 was also done in November 2010. There was a primary healing on the wound as a result of treatment. He was able to sit and stand as well as stay in upright position up to 2-3 hours. At the moment, mobility is restored, able to walk and sit. But pain is still present. Can we expect further surgical treatment and rehabilitation at your center?
...more
In this case surgical care rendered fully, but it is hard to say more without images. If pain is still present, it is necessary to look for the cause of this, but it may be in the early postoperative period. You can contact us for a consultation to clarify the nature of the disease.
MRI or CT scan
Please tell me what kind of examination is better in case of head injury - an MRI or CT scan. I have hit my head in June this year, and now I feel a discomfort at the site of the injury sometimes (there in no acute pain)?
CT has advantages in the visualization of bone structures. MRI is better for soft structures imaging, including the brain substance. According to the description, the intracranial structures damage is unlikely. Why CT or MRI? An ultrasound of soft tissues in the area of injury is also applicable. The pain in the
scull can also be associated with vessel, for example, cranial arteritis, or lymphadenitis, or muscle/enthesis, and then you might need certain blood tests. And maybe these tests are not required. I would recommend you to see the doctor and let him assess the case; he will take a decision concerning following examination as a result of consultation.
...more 
















.webp)

.webp)





