Osteoporosis of the spine
NarratesEvgeny Zhilyaev,
Professor, MD, Doctor of the highest category.
Osteoporosis is a systemic disease characterized by a decrease in bone density. In primary osteoporosis, the plates and tubules that make up the bone become thinner, while the mineral composition remains at the same level.
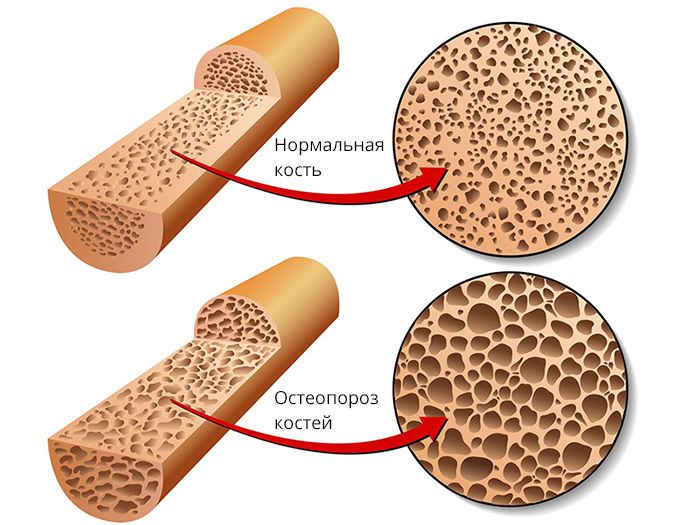
The development of osteoporosis depends on many factors, the most important of which is the lifestyle of a modern person. For example, rural residents rarely develop osteoporosis due to high physical activity, prolonged exposure to the sun, lack of vitamin D deficiency, and eating foods rich in calcium. Urban residents are not evolutionarily programmed for a modern pace and lifestyle. They are in conditions for which the human body was not originally designed. Lack of necessary physical activity, lack of vitamin D and calcium, and smoking are risk factors for developing osteoporosis. The prerequisites for the development of osteoporosis are laid at the age of 25-30. It depends on what bone density was achieved at this age, whether osteoporosis develops in the future or not.
Diagnostics
Osteoporosis usually develops asymptomatically (sometimes specific symptoms occur with severe osteoporosis of the spine), most patients are unaware of the presence of the disease. However, osteoporosis requires treatment in a clinic due to the high risk of bone fractures. Accordingly, the diagnosis should be targeted, and there are certain recommendations for the prevention and detection of osteoporosis in various groups of patients.
To detect osteoporosis, densitometry. This study is recommended for all women over 60 and men over 65. In addition, densitometry is indicated for all menopausal women who have one or more risk factors for developing osteoporosis.
Risk factors:
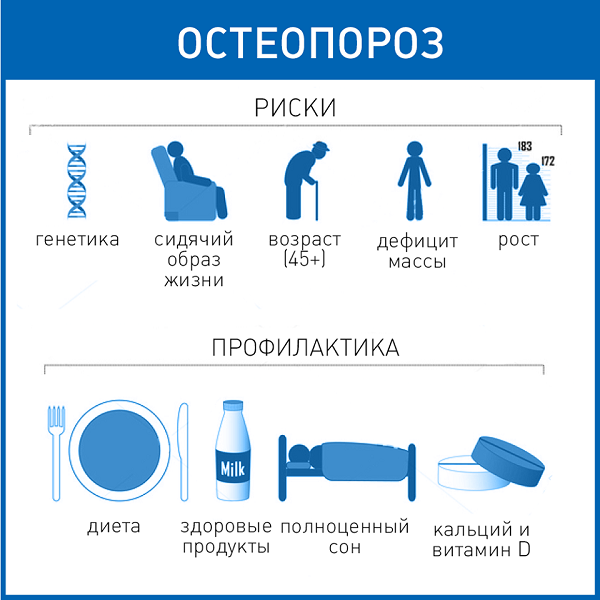
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Smoking.
- Physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle).
- Lack of vitamin D.
- The presence of fractures in the anamnesis, etc.
If the examination reveals osteopenia (a moderate decrease in bone mineral density), the patient needs constant dynamic monitoring and active prevention of osteoporosis. If bone density continues to drop, the patient is prescribed treatment.
Prevention of osteoporosis
Treatment of osteoporosis: the main stages.

- Non-drug therapy: increased physical activity. Exercise, walking, and swimming help strengthen bones and significantly reduce the risk of fractures. Under constant stress, growth factors are released in the bone, which contribute to the build-up of bone tissue. Physical activity, which is not associated with the risk of fractures, has a positive effect, including on the spine. The best option is walking: 4 times a week for 40-60 minutes. It has a stimulating effect on the spine and hip neck. Fractures of the femoral neck and vertebrae are the most dangerous in osteoporosis due to the frequent need for prolonged immobilization. An important role is played by teaching patients to prevent falls (organization of space in the apartment, the use of special devices when walking, a physical activity plan, training of the vestibular apparatus). If the patient has difficulty moving, has impaired coordination of movements, has muscle weakness, it is recommended to discontinue sedatives, which increase the risk of falling.
- Prevention (optimization of calcium metabolism). To slow down the development of osteoporosis and enhance the effect of prescribed medications, it is extremely important to normalize calcium metabolism. The patient's blood and urine should contain a normal amount of calcium. Calcium deficiency is most often manifested by a reduced daily excretion of calcium in the urine with a normal calcium content in the blood. The opposite situation is ideopathic hypercalciuria, a hereditary disease in which the kidneys do not retain calcium well. In both cases, the main task is to normalize calcium metabolism in order to eliminate its deficiency in the body.
-
Taking osteotropic drugs. Bone is one of the few tissues of the human body that is continuously being renewed. Osteoporosis disrupts the cycle of self-renewal, while the formation of new bone slows down to a greater extent than the destruction of the old one, so the bone content decreases over the years. Inhibitory drugs form the basis of the treatment of osteoporosis. Their effect is based on slowing down both the process of destruction and the process of formation of new bone tissue. But bone destruction is blocked to a greater extent than the formation of a new one. The most traditional and studied drugs in this group are bisphosphonates (alendronate, risedronate and zoledronic acid). Relatively recently, the genetically engineered drug denosumab has appeared, which also has the ability to block the activity of bone-destroying cells and reduce the risk of fractures. When inhibitory drugs are ineffective, a parathyroid hormone drug, teriparatide, is used. It accelerates the process of new bone formation. With short-term use, it provides a high increase in bone mineral density and a significant reduction in the risk of fractures. Its disadvantages are the need for daily subcutaneous administration and frequent side effects in the form of redness, itching and irritation of the skin at the injection site, therefore, teriparatide is rarely used today.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment. Annual monitoring of calcium metabolism. It is not enough to restore the metabolic process, it is necessary to regularly maintain its balance and monitor changes in indicators in order to adjust treatment in time. In addition, annual densitometry and radiography of the thoracic and lumbar spine are recommended for regular monitoring of the effectiveness of the treatment. The continued decrease in bone density or the appearance of new vertebral fractures may be the reason for a change in treatment tactics.
The treatment of osteoporosis at the European Medical Center (Moscow) is carried out in accordance with protocols adopted in leading medical centers in Western Europe, Israel and the USA. The EMC Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosisemploysneurologists, vestibulologists, ophthalmologists,orthopedic traumatologists,endocrinologists,rheumatologists and other specialists. Doctors work closely together, which allows for a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition and prevent the development of complications. A full range of care is available to patients, including the opportunity to receive a second opinion from leading foreign experts on this issue. EMC rheumatologists have experience working in leading clinics in Western Europe and Israel. If for any reason the patient cannot come to the clinic, an absentee consultation or an online video consultation of the doctor is organized.
Why the EMC
The first and only clinic in Russia, created in the image of the world's leading clinics
EMC is a multidisciplinary center offering patients a high level of medical services and a personalized approach
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Learn more
Learn more
Worldwide recognition and awards
 Certificates and licenses
Certificates and licenses
Make an appointment for a consultation
Specify your contacts and we will contact you to clarify the details
Reviews
and new products of the EMC


.webp)



.webp)


.webp)


.webp)


.webp)
.webp)

.webp)

