Sometimes multiple IVF attempts with oocytes that are good from the point of view of embryology fail: for example, an implanted embryo does not take root and dies.
Why can this happen? The morphology of the oocyte division spindle is of great importance.
The structure of the egg, and what is the spindle of division?
The quality of the embryo and its development potential depend on the quality of the oocyte. The shape of the cell, the structure of the cytoplasm, the shell and the polar body (the cell separating from the oocyte during maturation) are usually evaluated. The egg itself may have an abnormal shape – oval or amorphous. The cytoplasm may have vacuoles (cavities inside the cell filled with cell juice), various inclusions, and an abnormal shape. The oocyte shell can be thick, thin, or carry any abnormalities: the polar body may be absent, fragmented, or located separately from the cell itself. All these anomalies affect the further development of the embryo to varying degrees.
There is another very important element in the oocyte – the spindle of division (Fig.1).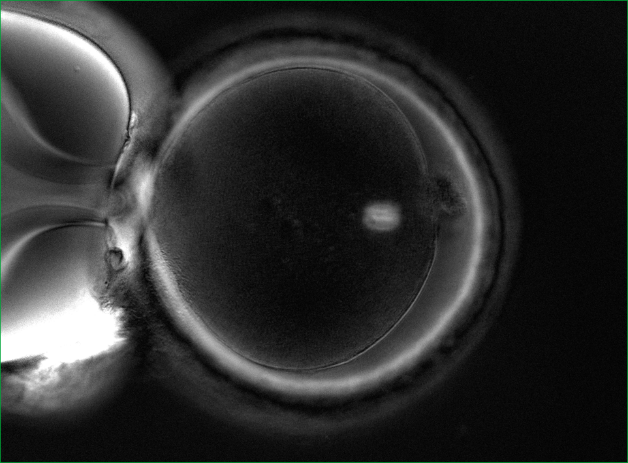
Who is shown the procedure for evaluating the division spindle?
1. For patients aged 40+. It is a well-known fact that with age, the percentage of oocytes with problems with chromosome separation increases. These problems lead to genetic mutations.
2. Patients with a large number of oocytes and poor embryo development (in particular, polycystic ovary syndrome).
3. Patients who have had multiple IVF attempts with good eggs from the point of view of embryology, but with embryos that do not take root after transplantation, or with early pregnancy losses.
How can the division spindle be evaluated?
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2).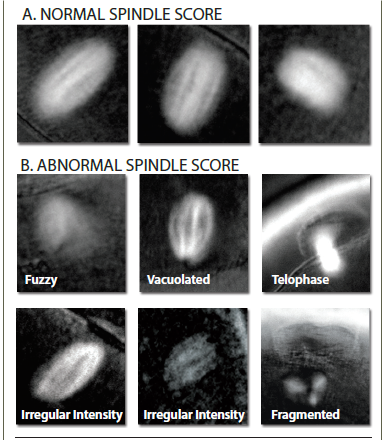 If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).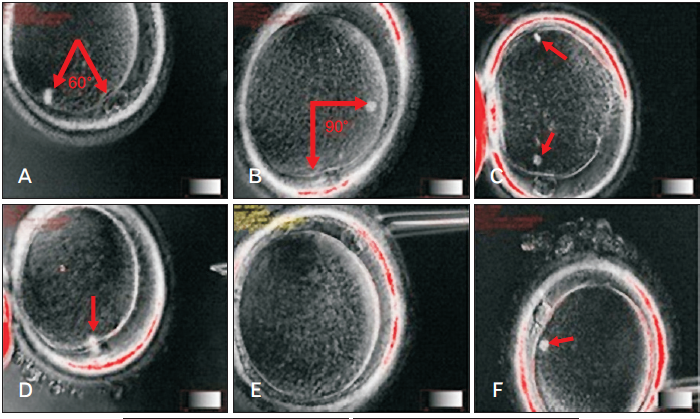 And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.

Who is shown the procedure for evaluating the division spindle?
1. For patients aged 40+. It is a well-known fact that with age, the percentage of oocytes with problems with chromosome separation increases. These problems lead to genetic mutations.
2. Patients with a large number of oocytes and poor embryo development (in particular, polycystic ovary syndrome).
3. Patients who have had multiple IVF attempts with good eggs from the point of view of embryology, but with embryos that do not take root after transplantation, or with early pregnancy losses.
How can the division spindle be evaluated?
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2). If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3). And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2). If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3). And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.

 And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.
Was this information helpful?
Questions and answers
How can you tell true contractions from false ones during pregnancy?
Only a doctor can tell true contractions from false ones after an examination and additional tests.
Is there a better sleep aide i can get other than what I have been using over the counter
Is there a better sleep aide i can get other than what I have been using over the counter. I know getting Ambian is a big hassle but is here something in between? I've been using Ambian for about 10 years almost daily, if it matters.
Ambian is a one the brand names of Zolpidem. It's available in Russia. You can schedule appointment with neurologist (Dr. Maslak, for example) and doctor will do prescription for you ( for Zolpidem or maybe another sleeping pill).
Rhinoplasty after 40
I would like to do a rhinoplasty, but it is said in some sources that “rhino” is not indicated after 40.
Good afternoon, Lydia. Rhinoplasty is allowable in your age. Dr. Levine, for example, performs rejuvenation in conjunction with rhinoplasty. The human nose grows throughout life. It becomes longer and more unattractive in adulthood. The rhinoplasty in conjunction with a facelift helps to achieve more pronounced
results of rejuvenation.
...more .webp)
Levin Sergey
08 September 2016
What to do first
What should I do first: Laser Fraxel and then the fillers, or Vice versa?
Good afternoon, Larisa. It is usually recommended to start with laser rejuvenation techniques, and then "polish" the result with hyaluronic acid injections. We invite you for a consultation. You can make an appointment by tel.: + 7 (495) 933 -66-54

Karapetyan Marianna
08 September 2016
Malignant kidney tumor
CT scan revealed a malignant kidney tumor in my brother. The tumor size is 3x7, which corresponds to stage 2. Tell me, please, how long does it take for such a tumor to be developed? And is it possible to remove the tumor surgically (total kidney removal)?
For a more precise answer we need to assess patient’s CT scans ourselves. At the EMC’s Urology clinic, both total and partial kidney removal with tumor is performed using the da Vinci robot. These surgeries are very gentle with fast postoperative recovery.
Prostate cancer
I am 74 years old. Prostate cancer was diagnosed. Total PSA was 25.8 ng/ml. Outpatient check-up was carried out. Are "Zoladex" injections enough? Biopsy revealed moderately poorly-differentiated small-acinar prostate adenocarcinoma. Where to start?
You should start with an extended examination, namely: skeleton scintigraphy, pelvic MRI, oncological examination. If the results of these tests will be the normal: surgery or radiotherapy may be offered (both with/without “Zoladex” therapy). If the results are abnormal: radiation therapy with/without “Zoladex”
therapy or “Zoladex” therapy may be offered.
...more
How to lose weight correctly
I am 53 years old, my weigh is 116 kg. In 1988, my metabolism was probably, disturbed following the first childbirth. I gained weight, and since then I have been trying to fight with it periodically. I eat a lot of sweets however glucose is now normal and it always was. With age, my legs and back started to hurt me,
it is hard to “move” myself. I have undergone an examination in the district hospital, but nothing special was found. What tests and examinations I should bring to the doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment? Thank you!
...more Unfortunately, doctors not always can find the cause of excess weight. But this does not mean that there are ways to deal with it. Of course, it is not easy, but you definitely should try! At the first consultation it is desirable to have blood tests results, obtained no more than 6 months ago, total cholesterol,
glucose, glycated hemoglobin. Notes in the diary of blood pressure for 1-2 weeks are also important. Most likely, the doctor will arrange some additional examinations at visit, but everything is very individual and it's better to discuss all details with the doctor personally. You surely have to bring the results of previous all examinations with you.
...more 
Novikova Polina
08 September 2016
Question about ultrasound
I am 36 years old. Thyroid gland ultrasound: topography: position is regular, the right lobe is enlarged W-24 mm, t-22 mm, l- 51 mm, the volume is 12.90 cm3, left lobe enlarged, W -23 mm, t-23 mm, l-56 mm, volume is 14,90 cm3, isthmus thickness is 5 mm, the total volume is 27.09 cm3, alignments are even,
echostructure is inhomogenous, echogenicity is normal, focal masses are not seen, lymph nodes are not seen, conclusion; ultrasound signs of diffuse changes in the enlarged thyroid gland. TSH 2.10 mcIU/ml (normal range 0.30-4.00). The doctor prescribed Iodocomb 50/150 for 3 months. I have been taking the medicine for 2.5 months, but TG does not seem to diminish in size and I feel discomfort (it’s like a need to stretch my neck). Whether the treatment prescribed is correct? Are any additional tests needed? Should I have my thyroid gland diminished for those 2.5 months or it is too early to talk about it? Thank you!
...more It's hard to advice any treatment by correspondence. The cause of the thyroid gland enlargement is still unclear based on the results provided. The most common cause is iodine deficiency and Iodocomb treatment is appropriate in this case. Another cause is a chronic autoimmune thyroiditis which requires different
treatment. Endocrinologists at EMC will advise you and decide on the types of treatment and necessary doses.
...more 
Russ Irina
08 September 2016
Arthrosis
My left jaw started to hurt me after giving birth. The pain was accompanied by a crunch, clicks, discomfort when chewing. Arthrosis was diagnosed at local institution. What should I do?
The symptoms of pain and the crunch may occur following precipitating factors. It can be a trauma of the maxillofacial area, ENT-organs infections, sitting with mouth open for a long time when visiting the dentist, hypothermia, overload. Perhaps, pregnancy and childbirth were such a factor in your case. The treatment
goal in arthrosis is to reduce the load in temporomandibular joint. Treatment depends on the cause or the complex of causes that triggered the arthrosis. This may be due to the anatomical mismatch between the articular head size and the glenoid fossa. This also can be due to the long-term overload resulted from irregular bite and muscle imbalance. If increased tone of the masticatory muscles has led to increased abrasion of teeth, method of treatment with the restoration of the chewing surfaces and cutting edges of all teeth is optimal. But before that, splint therapy (mouth guards) is mandatory, which ensures the optimal position of the articular heads in articular fossae. Treatment is designed depending on the cause of changes in the joint. If the irregular bite is present pre-treatment by the orthodontist may be worthwhile.
...more
Problems with teeth
I have a huge problem with my teeth - all the teeth were treated, metalless ceramics were fixed in some places, a few teeth need to be removed. The treatment was carried out abroad, but the caries problem was beyond control, despite regular professional hygiene and specially selected tools. What range of dental
examinations, in addition to specialist’s consultation, I can count on in EMC Moscow?
...more Various dental diagnostic methods are available in our Dentistry Department: computed tomography of all teeth of both jaws, which gives a three-dimensional image and allows the doctor to more accurately diagnose; orthopantomography gives a flat image of all the teeth; the targeted x-ray tooth image. Tooth extraction
is performed surgically, mostly under local anesthesia. Diagnostic and treatment methods are determined individually by the attending doctor on consultation. Thank you for your message!
...more
How soon I may drive after LASIC?
When can I ride a car after LASIK?
Eyesight recovery is quite fast. Visual acuity is almost completely restored next morning, and most people can drive a car and get to work.

Elias Raid
08 September 2016
Sudden rises of blood pressure
How to stabilize sudden rises of blood pressure, accompanied by nausea and vomiting in a patient with chronic hypertension (it is not always clear what comes first - nausea and vomiting and, as a consequence, the blood pressure increase, or Vice versa).
An adjustment of appropriate permanent antihypertensive therapy is required for blood pressure to be stabilized. It is best to schedule a consultation with the cardiologist and undergo heart ultrasound, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring and ECG. You can make an appointment by phone +7 (495) 933-66-55. Specialists of
the Cardiology Department will be happy to help you.
...more
Extrasystoles
Extrasystoles appeared on my husband’s ECG following smoking cessation. He has a serious intension to undergo a thorough examination. What kind on up-to-date methods are used in your clinic?
EMS offers the most up-to-date methods of examination for your husband to clarify the nature of arrhythmias. ECHO-cardiography, 24 hour Holter monitoring ECG, loading tests, and, if needed, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring as well as all laboratory tests are available at EMC’s cardiology department. There is an
option to undergo a comprehensive examination under the program "Health Status after 40", which includes specialists' consultations, diagnostic laboratory and instrumental tests. We will be happy to help you. You can make an appointment by phone +7 (495) 933-66-55.
...more 
Dyagileva Mariya
08 September 2016
How soon another attempt is possible?
Twin pregnancy resulted from IVF, but cervical dilatation occurred and water broke at 20 weeks, so the pregnancy was not maintained. How soon another attempt is possible?
At least a year interval between childbirth and repeated IVF program is required. It is advisable to be prepared and to make every effort to get a singleton pregnancy.
Рolyp of the cervical canal
Hysteroscopy revealed a polyp of the cervical canal, it was removed, but there are plenty of micropolips. May I do IVF or they should be treated?
Usually, all polyps are removed at therapeutic and diagnostic hysteroscopy. It makes no sense to leave them in the uterus cavity. I think that if manipulation such as "Hysteroscopy with separate diagnostic curettage" was done, you have no polyps now and may safely prepare for IVF.
Рancreatic cancer
My wife of 64 years was diagnosed with pancreatic cancer in the autumn of 2014. Stage 4 was concluded. Surgery is impossible. There is a massive thrombosis. Three biopsies were carried out. A benign tumor was revealed. She lost a lot of weight. An episode of severe pain took place about one month ago. Currently, a
significant problem is the ascites, swollen legs; food is poorly digested, general discomfort. What can you recommend? Is it necessary to remove the fluid and what might be the consequences?
...more The picture you described is consisted with the concept of "metastatic ascites". Laparocentesis is appropriate as a therapeutic and diagnostic approach. Given the negative cytology, it is likely that the patient has a neoplastic disease of the colon, ovaries or stomach. Our experts will hold a consultation on the
same day and perform the procedure to verify the diagnosis and consider the possibilities of palliative treatment.
...more 
Pavel Koposov
07 September 2016
Break iafter the last course of chemotherapy
Why a break is necessary after the last course of chemotherapy?
In cases where chemotherapy is not enough effective, some cells of the tumor does not die as a result of exposure and only slow down their biological processes temporarily, so they do not accumulate diagnostic radiopharmaceutical that can lead to a false negative result. After 2-3 weeks, tumor cells return to their
normal state and can be seen at the PET/CT scan. Thus, the break after the last course of chemotherapy should be done in order to obtain reliable results of the quality of treatment.
...more
Radiation therapy for prostate cancer
What to expect during radiation therapy for prostate cancer?
The procedure of external radiotherapy is similar to conventional x-ray examination. Radiation is invisible, has no smell and gives no sensations, side effects do not appear until 2nd or 3rd week of treatment.
Radiotherapy for prostate cancer is a local treatment; therefore, you may experience some side effects
only in those parts of the body that are exposed.
...more
Сhronic nonspecific spondylitis
Can we go to your center in the following case: the patient born in 1955. Diagnosis: chronic nonspecific spondylitis T7-T9. A state after interbody fusion T7-T9 with autologous bone. Brown-Sequard's syndrome. Right thoracotomy with interbody fusion using autotransplantation (resected rib) was done in 2010, no bone
block formed during the postoperative period. Transpedicular fixation T 5-6-10-11 was also done in November 2010. There was a primary healing on the wound as a result of treatment. He was able to sit and stand as well as stay in upright position up to 2-3 hours. At the moment, mobility is restored, able to walk and sit. But pain is still present. Can we expect further surgical treatment and rehabilitation at your center?
...more
In this case surgical care rendered fully, but it is hard to say more without images. If pain is still present, it is necessary to look for the cause of this, but it may be in the early postoperative period. You can contact us for a consultation to clarify the nature of the disease.
MRI or CT scan
Please tell me what kind of examination is better in case of head injury - an MRI or CT scan. I have hit my head in June this year, and now I feel a discomfort at the site of the injury sometimes (there in no acute pain)?
CT has advantages in the visualization of bone structures. MRI is better for soft structures imaging, including the brain substance. According to the description, the intracranial structures damage is unlikely. Why CT or MRI? An ultrasound of soft tissues in the area of injury is also applicable. The pain in the
scull can also be associated with vessel, for example, cranial arteritis, or lymphadenitis, or muscle/enthesis, and then you might need certain blood tests. And maybe these tests are not required. I would recommend you to see the doctor and let him assess the case; he will take a decision concerning following examination as a result of consultation.
...more
Lump in my breast
I have noted the lump in my breast periodically appeared following breastfeeding my first child (as a result of plugged duct). I did an ultrasound, but it revealed nothing, as if everything was normal. I knead my breast periodically and feel pain at those moments. Now I am pregnant, due date is on 20th. What should I
do?? When to examine my breasts, is it possible to perform the examination during pregnancy and lactation?
...more The "lump" in the breast cannot occur after feeding, even if it was the plugged duct. You should not "knead" the breasts. If there is a problem or even if you think it is – the breast should be examined. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are not contraindications for this. Under normal conditions for pregnant women we
recommend a breast examination during 1 and 3 trimester (before childbirth). There are no contraindications for breast examination in your case. You are welcome at any convenient time for examination and advice on breastfeeding.
...more
Benign disease
I have a benign lump in one breast size of 12.0*9.9 mm. Puncture or a biopsy will be done next week. I was told by mammologist that surgery is needed. As far as I know, concerning the surgery, axillary lymph nodes are to be removed together with the tumor. I also know that in Europe lymph nodes are testes for
specific markers and only affected ones should be removed; if lymph nodes are no affected, they are not to be dissected and the surgery is minimally invasive. So what is your approach? Does it make sense to do it or you have the same methods and the same equipment?
...more If histological examination of the sample reveals fibroadenoma of basic type or tissue hyperplasia without atypia, or nodular type fibrocystic condition of the breast tissue, the question of surgical treatment should not arise. If biopsy reveals giant fibroadenoma sectoral resection is indicated, i.e. mass excision
within the healthy tissues and lymph nodes will be removed. In case of non- benign histological result, i.e. carcinoma is detected, subsequent immunohistochemical examination is required as well as a clinical oncologist and surgeon consultation; and the decision on complex treatment will be taken by case management team. With regard to the diagnosis and treatment methods in our center, each case is addressed individually. Sometimes we remove a benign area (for example, the area of hyperplasia with atypia) using the vacuum-needle technique through 3-4 mm incision. As for the surgical procedure protocols for benign breast tumors, benign simple fibroadenoma is not removed in America, Europe, Israel, etc. I would like to discuss your case with you in more details and perform some additional tests if needed, so I would be glad to see you at EMC’s Breast center.
...more
Melanoma
My mom had a mole (suspected for melanoma) removed in November 2015. Histology revealed lentigo melanoma in situ. We checked the slides back in the Netherlands, and the diagnosis was a superficial spreading melanoma of Clark 3 Т1а Beslow 0,8 stage; re-excision with capture of 1 cm of healthy skin is recommended. Is
it possible to make re-excision and subsequent histology in your hospital? If so, how soon?
...more We absolutely agree with the opinion of the European colleagues: re-excision with a wider offset is required; according to the Russian Protocol it is necessary to move 2 cm from the peripheral edge. This is for counter insurance, as lentigo-melanoma is a favorable type, and previous surgery is likely to put an end to
this story and the forecast is favorable. All the necessary manipulations for the study are possible in our Clinic; we have our own well-equipped laboratory with the possibility to ask the advice concerning the sample in Germany and Israel.
You should make an appointment with the surgeon-oncologist (Marina Bissessar) in the nearest time to conduct the diagnostic re-excision. Hope to help!
...more
A spot on the back and chest
I have a spot on the back and chest, what could it be?
A spot on the skin is one of the most common symptoms of various skin diseases. Infectious (viral, bacterial or fungal) as well as noninfectious skin including serious diseases and nevi (moles or birthmarks) can manifest as spots on the skin. You should go to the dermatologist for accurate diagnosis. The doctor will
examine you and, if necessary, a special instrument (Dermatoscope, wood lamp) will be used. A skin scraping can also be done in the lesion for microscopy, cytology or culture. A treatment will be prescribed after diagnosis.
...more 
Batkaeva Nadezhda
07 September 2016
Uterine cancer
My mom was diagnosed with the uterine cancer. She is 68 years of age and has an obesity of 4th grade (the growth of 166 cm, weight 135 kg) and hypertension. Admission to the radiology department was recommended. What should we do? As far as I know the surgery is the only method for cancer of the uterus to be removed.
Is it really so that this surgery is only possible for young and relatively healthy persons?
...more It is not quite so. We can operate on any patient, but the issue is which complications can lead to patient’s death and which of them can just delay the recovery. From the anesthesiologist’s point of view, it is a major challenge to intubate patients with 4th degree obesity; the abdominal section is also possible,
but there is a 100% risk of suture line disruption and inflammation, let alone the postoperative pneumonia, venous thrombosis, etc. There is another option such as vaginal hysterectomy which is more acceptable and relatively safe in obese patients. It is not a «treatment standard», however, as it allows not obtaining pelvic washings, but still there is a possibility of complete cure. Anesthesia remains a problem - both general and spinal. Radiation therapy without surgery is another acceptable treatment option besides vaginal hysterectomy. A chance of complete cure is still exists, but the survival rate is on average lower than in surgical treatment
...more 
Vladimir Nosov
07 September 2016
Dermoid cyst and pregnancy
An ultrasound revealed a mass in my left ovary during the first pregnancy. I was told that it is a dermoid cyst. Five years have passed since then. I gave birth to a second child. An ultrasound was performed annually. There were differences in size, but not significant. Since I’m going to have the 3rd child, another
ultrasound was done today. The doctor said that the cyst had increased. I am concerned about it. Don't know where to start. What tests are needed? Thank you.
...more Surgical treatment is strictly indicated in your case given the long history of the mass in the ovary and its rapid growth in recent times. In our clinic, we perform such an intervention laparoscopically through 3 small punctures. Patients go home next morning after the surgery and may return to work after 3 days.
This surgery must be as delicate to preserve healthy ovarian tissue (considering your reproductive plans) as radical at the same time to remove the mass together with the capsule. At the preoperative stage an expert level ultrasound with Doppler is required, as well as blood tests for Ca-125 and НЕ-4 tumor markers. The decision concerning the necessity of FEGDS and colonoscopy is taken based on the results of these tests.
...more
Total knee replacement
My mom suffers from gonarthrosis for the past three years. Despite treatment by injections the pain is still present. MRI revealed a meniscal tear in the posterior horn, the presence of small bony osteophytes on the patella, a small amount of fluid in the joint cavity (signs of exudative synovitis were detected)
joint space is asymmetrically narrowed in the medial segment. The pain is ongoing but the knee remains flexible. Tell me, please, whether the surgery is contraindicated for meniscal tear in case of arthrosis? Is it possible to do an arthroscopic surgery on the meniscus in our case or it should be «major» surgery? And what would you advice concerning knee replacement for the patient in the age of 57? What is the life time of the artificial joint?
...more It is necessary to make an X-ray of the knee in direct projection in standing position. If it turns out that there is no medial cartilage in the medial area, then the knee replacement is the only solution. The age of 57 is normal for the prosthetics. Modern artificial knee joint (when properly placed of course) will
serve for a lifetime. You can make an appointment via phone +7 (495) 933-66-44.
...more 
Kardanov Andrey
07 September 2016
Pain
I am 19 years old, professionally engaged in weightlifting. I did an arthroscopy of both knee joint a year ago, now feel pain in them and it prevents me from training at full capacity. I visited a traumatologist, and «osteoarthritis of 1 degree» was diagnosed. Could you advise me some medicines or anything else to
relief the pain? Thank you very much for the answer!
...more
First of all you should undergo an MRI and find out what was done at arthroscopy; if it’s really an arthrosis of 1 degree, hyaluronic acid injections are possible and physiotherapy is not required. Anyway, you are always welcome to consultation for thorough examination.
Question to Dr. Yakobashvili
Tell me, please, at which age child's hearing should be checked-up if we were informed at the hospital before discharge that one ear does not hear. At the moment the child’s age is 1.5 months. Thank you.
These tests done in the hospital are often false negative. Hearing can be tested now, it is necessary to make an appointment to the audiologist.
Cought
A child of 11 years old, suffers from cough for more than six months. The cough is dry, sometimes attack-like, mainly begins during the day, and often occurs before sleep. There is no cough at night. CBC is normal, glucose is 4.16, total IgE 111.80, Toxocara, Ascaride are negative, Cytomegalovirus, Mycoplasma are
negative, PPD test is negative as well. A chest x-ray is normal. We have already consulted with a therapist, otolaryngologist, pulmonologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist... the cough is still present. What should we do?
...more First of all, there are no results of whooping cough testing among the results provided above. The disease cannot be ruled out, even if your child was vaccinated. The blood test for antibodies against the whooping cough germ is required (blood test for class M and G antibodies against Bordetella pertussis). Second,
even a slight increase in class E antibodies is a reason to visit an allergist and to perform an evaluation of respiratory function with bronchodilator. This method will detect a latent bronchial spasm in your child. Even if the results of the test will be normal, allergologist mast rule out the allergic nature of the cough even if it's not obstructive syndrome. Third, this cough can be due to gastroesophageal reflux. It is difficult to draw any conclusions having no data of gastroenterologist’s consultation. 24-hour acidity monitoring of the stomach and esophagus is carried out to confirm or exclude the presence of reflux. Fourth, you didn’t mention whether x-ray of nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses was done. Perhaps, after all, the pathology is associated with ENT organs.
...more
How to stop dreaming?
Can you tell me if there are any medications that stop a person dreaming? I have been dreaming constantly for a long time, and the dreams are always vivid and emotionally charged. I wake up tired, not wanting to do anything, and I feel only lethargy and apathy. I live in another city.
We have all the tools for an accurate, comprehensive diagnosis, and medical treatment of such conditions, as well as psychosocial rehabilitation, which is critical for returning to an active lifestyle. The support program includes modern methods of diagnosis, regular professorial meetings, and comprehensive
psychological and neurocognitive support. Unfortunately, all the necessary diagnostic and therapeutic interventions can only be done with the patient being present at the Clinic. We are ready to welcome you to the EMC. Inpatient and outpatient psychiatry clinics operate within the multidisciplinary hospital, which creates the most comfortable conditions for patients.
...more 
Rivkina Natalya
09 November 2015
Baby teeth - treat or not?
Baby teeth do not need to be treated, because they will drop out in any case - is it true?
If the teeth are not cleaned properly white carious spots will appear underneath the soft plaque. This initial stage of decay is reversible: with proper hygiene the stain will gradually fade. The next stage is when the defect appears: the integrity of the enamel (the outer shell of the tooth ) is broken and a
cavity appears in the tooth . From this moment caries begins to develop more rapidly since the dentin (the hard tissue of the tooth located under the enamel) is less dense than enamel, and it becomes difficult to clean the teeth properly.
If microorganisms get into the cavity of the tooth where the nerve passes, this will cause pulpitis - inflammation of the pulp of the tooth (the pulp consists of blood vessels and nerves), which may be accompanied by pain, but in the milk teeth is usually asymptomatic.
Pain may occur later, when the nerve has died completely and infection occurs outside the tooth - in the bone. In addition to pain, pulpitis is sometimes accompanied by swelling of the gums, fistulas (channels between the foci of the infection and the gum) and loose teeth .
The pathological process - from the appearance of a white spot to the development of inflammation outside of the tooth root - can be fast and take a few months or last for years, depending on many factors.
To avoid problems with your child’s teeth , you should visit the paediatric dentist regularly. The first appointment with the dentist should be when the child is 1.5 years old. Following on from this there should be regular check-ups every 6 months, or more frequently as directed by the doctor.
...more
Diagnosed infertility - what to do?
I’m 27 years old, diagnosed infertility since 5 years ago, tubal factor and only one working ovary. Have gone through 3 tries of in vitro fertilization, one was stimulated, had no response, in all 3 cases I had only one oocyte. AMH 0,91. Do you think I have a chance for a pregnancy with my own oocyte? Sperm quality
is good.
...more
Yes, of course, you should fight for your oocytes. There is a variety of minimal stimulations: modified cycles, natural cycles etc. If these methods don’t work, so we will think about donor cells. But you must definitely give your ovaries a chance.
Severe cervical dysplasia
I have a transplanted kidney and I was recently found to have severe cervical dysplasia. The biopsy results are not yet back, but the physician says I must have my uterus and cervix removed. My question is: Can I have the operation in your clinic?
For severe cervical dysplasia, usually cervical conization is sufficient. If you have no plans for reproduction, or you already have children, then theoretically you can discuss having a laparoscopic removal of the uterus and cervix, but these decisions should not be made through correspondence. If you have a
referral for an operation in the city where you live, and have the opportunity to come to Moscow, come for a free consultation using "Second Opinion" promotion. If necessary, we can quickly provide operative treatment at a discount.
...more 
Vladimir Nosov
09 November 2015
Emergency's Working Hours
What are your hours?
We are open seven days a week, 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
Nonbacterial Prostatitis
For over a year now I have suffered with nonbacterial prostatitis. I am 65 years old and my prostate is 50 cubic cm. I have treated this every way possible to no avail. As I understand it, there are only 2 possibilities: 1) Daily painkillers and sleeping pills which leave me in a drug-induced stupor. 2) Radical
prostatectomy, although I don't have cancer and my PSA is around 1. I don't live in Russia and it isn't possible to have a radical prostatectomy here. Can I have this operation in your center? Because of the severe inflammation, I can only sit and walk for limited amounts of time. I am near insane from the constant pain and sleeplessness.
...more
As with all civilized urologists in the civilized world, we COMPLETELY remove the prostate ONLY in cases of prostate cancer. At the same time, if you would like to be seen by us for assistance, at your convenience we can examine you and treat your problem.
Both knees
I would like to get MRT and diagnosis for my knees. Left has old trauma and right is hurting now permanently. An English or German speaking doctor would be an advantage. KR Florian
Dear Florian. Be sure you'll get all the answers for your questions. We have MRI and English-speaking staff including knee surgery specialists. Our assistants will contact for further instructions. Kind regards.
Laser surgery for removal of varicose veins
Does you clinic offer laser surgery for removal (or correction) of varicose veins on the legs? I would like to learn about both the aesthetic and medical side of the issue.
Our clinic performs the most common and advanced methods of varicose veins’ treatment. This includes classic phlebectomy, injection sclerotherapy, and foam sclerotherapy (the most common method of treatment in Europe). The method of treatment depends on certain medical conditions. If the disease manifests itself as
small spider veins, the laser correction could be performed by a surgeon-phlebologist or a dermatologist. But each case is always individual. You need to make an appointment for a consultation to discuss all the issues in more detail.
...more
Cancer of the thoracic spine
I have cancer of the thoracic spine. According to the MRI, I have wedge-shaped vertebrae, and small fractures in some places, with the absence of normal bone. Is it possible to undergo a vertebroplasty if the lumbar region is also affected? Will the lumbar vertebrae be able to support the thoracic vertebrae after
this procedure?
...more
It is necessary to analyze the MRI scans in this case. Metastatic vertebral bodies are treated with radiation and chemotherapy according to our principles. Vertebroplasty is possible, but it is difficult to say anything specific without seeing the scans.
Hernia-related pain
Hello, I had hernia-related pain about one month ago. With abrupt leg and foot movements, I experience pain in the cervical segment of the spine, radiating into my arm. MRI test result: degenerative-dystrophic changes of the cervical segment, spondylosis, osteophytosis of C5-C6 segment, posterior hernia of C4-C5
segment with a tendency to sequestration. Could the hernia growth be stopped? What do I do?
...more If the MRI data shows a disk protrusion (small hernia) which does not cause dural sac compression and you have no clinical manifestations of the disease, you need to undergo physical therapy and therapeutic physical training aimed at strengthening the muscles of the cervical segment of the spine. In order to make the
decision, you must make an appointment and show the MRI results to a neurologist or neurosurgeon, who will give you recommendations for further action. You can get all necessary assistance at our center.
...more
Tumor in the breast
I’ve had a tumor in the lower part of my right breast and a metastasis in the left lymph node removed in 2011. I then had a recurrence in the upper quadrant of the right breast. But the doctors didn’t immediately react to this, even though I told them that I was experiencing some discomfort. After this I had biopsies
under ultrasound guidance at several medical centers, but I keep getting a completely different diagnosis everywhere I go. I still haven’t received any treatment. Test results are good. The metastasis is not growing but just sitting there. They’ve suggested a mastectomy. What’s the point? I don’t want to undergo chemotherapy. I’m on a raw food diet. I don't know what to do. I wish at least one of the diagnoses was confirmed. I want to be sure that I’m getting the right treatment. Because it’s the doctors that have brought me to this situation, even though I’ve had regular screenings for the past 25 years.
...more Before answering any questions regarding treatment, it is necessary to carry out a successful biopsy under ultrasound or X-ray guidance, to obtain multiple tissue samples (not cells) with subsequent histological and immunohistochemical analysis. Only then can we discuss a specific treatment plan! In any case, EMC
staff are always ready to provide advice and carry out the necessary diagnostic tests.
Best regards, Irina Vassilieva — M.D, radiologist, Head of EMC Breast Clinic
...more 









.webp)









.webp)

.webp)


