Sometimes multiple IVF attempts with oocytes that are good from the point of view of embryology fail: for example, an implanted embryo does not take root and dies.
Why can this happen? The morphology of the oocyte division spindle is of great importance.
The structure of the egg, and what is the spindle of division?
The quality of the embryo and its development potential depend on the quality of the oocyte. The shape of the cell, the structure of the cytoplasm, the shell and the polar body (the cell separating from the oocyte during maturation) are usually evaluated. The egg itself may have an abnormal shape – oval or amorphous. The cytoplasm may have vacuoles (cavities inside the cell filled with cell juice), various inclusions, and an abnormal shape. The oocyte shell can be thick, thin, or carry any abnormalities: the polar body may be absent, fragmented, or located separately from the cell itself. All these anomalies affect the further development of the embryo to varying degrees.
There is another very important element in the oocyte – the spindle of division (Fig.1).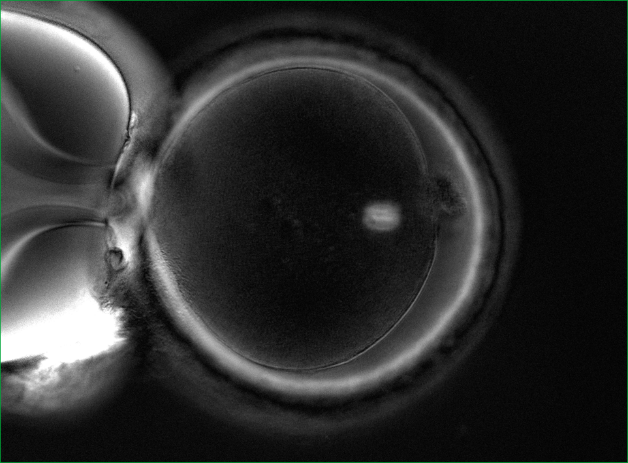
Who is shown the procedure for evaluating the division spindle?
1. For patients aged 40+. It is a well-known fact that with age, the percentage of oocytes with problems with chromosome separation increases. These problems lead to genetic mutations.
2. Patients with a large number of oocytes and poor embryo development (in particular, polycystic ovary syndrome).
3. Patients who have had multiple IVF attempts with good eggs from the point of view of embryology, but with embryos that do not take root after transplantation, or with early pregnancy losses.
How can the division spindle be evaluated?
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2).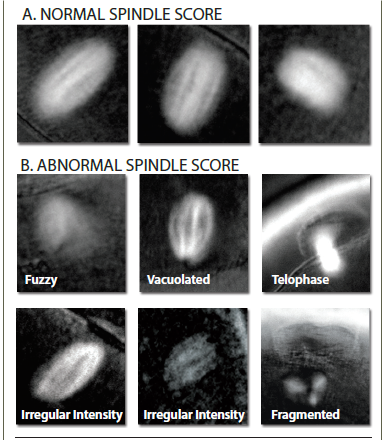 If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).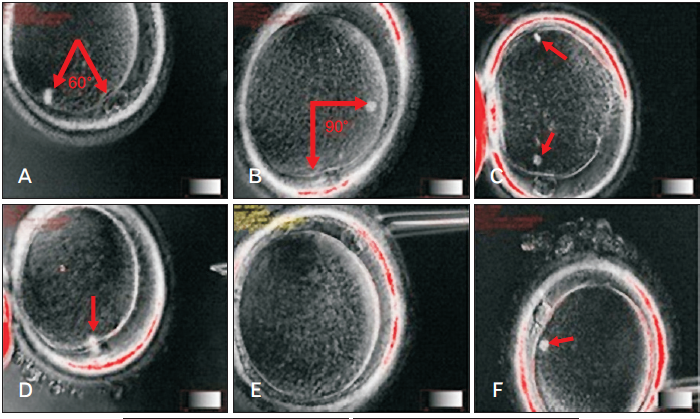 And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.

Who is shown the procedure for evaluating the division spindle?
1. For patients aged 40+. It is a well-known fact that with age, the percentage of oocytes with problems with chromosome separation increases. These problems lead to genetic mutations.
2. Patients with a large number of oocytes and poor embryo development (in particular, polycystic ovary syndrome).
3. Patients who have had multiple IVF attempts with good eggs from the point of view of embryology, but with embryos that do not take root after transplantation, or with early pregnancy losses.
How can the division spindle be evaluated?
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2). If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3). And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.
It is impossible to see it with a conventional microscope, so no one evaluates it in routine practice. It is necessary to have a special polarizing installation for visualization. In world practice, only a few clinics have the necessary equipment in their arsenal and evaluate the spindle of division.
The importance of the quality of the division spindle in fertilization
The spindle of division can be either normal or abnormal. Normally, it should be clearly visualized and located close to the polar taurus. But there are various anomalies: vacuolization, the spindle is broken into fragments, poorly visualized, and may be completely absent (Fig. 2). If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3).
If the oocytes have a normal division spindle, the fertilization efficiency is 90%, and the embryo yield is 76%. In case of abnormal fertilization, the efficiency of fertilization is 72%, and the yield of embryos decreases to 31%. The probability of implantation of embryos that were obtained from oocytes with a normal spindle reaches 60%.
The size of the division spindle is also important. With a fission spindle from 90 to 120 microns2 , the chances of pregnancy are highest.
And one more important point: at the time of ICSI (injection of sperm into the cytoplasm), the embryologist must correctly position the oocyte. Usually, the marker is the polar body, under which the spindle of division should theoretically be located. In order not to damage the spindle, the oocyte is oriented for 6 or 12 hours, to maximize the removal of the spindle from the injection site. However, the spindle can be positioned in a cage in different ways (Fig. 3). And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
EMC capabilities in the evaluation of the division spindle
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.

 And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
And since it is impossible to see the spindle during routine ICSI, there is a high probability of damage to it. The imaging system of the division spindle used in the EMC minimizes the risk of damage to it.
Specialists from the EMC Clinic for Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine conduct a detailed assessment of the spindle division. For this purpose, the European Medical Center has all the necessary equipment and experienced specialists who have worked and trained in leading clinics in Europe.
Was this information helpful?
Questions and answers
Dermoid cyst and pregnancy
An ultrasound revealed a mass in my left ovary during the first pregnancy. I was told that it is a dermoid cyst. Five years have passed since then. I gave birth to a second child. An ultrasound was performed annually. There were differences in size, but not significant. Since I’m going to have the 3rd child, another
ultrasound was done today. The doctor said that the cyst had increased. I am concerned about it. Don't know where to start. What tests are needed? Thank you.
...more Surgical treatment is strictly indicated in your case given the long history of the mass in the ovary and its rapid growth in recent times. In our clinic, we perform such an intervention laparoscopically through 3 small punctures. Patients go home next morning after the surgery and may return to work after 3 days.
This surgery must be as delicate to preserve healthy ovarian tissue (considering your reproductive plans) as radical at the same time to remove the mass together with the capsule. At the preoperative stage an expert level ultrasound with Doppler is required, as well as blood tests for Ca-125 and НЕ-4 tumor markers. The decision concerning the necessity of FEGDS and colonoscopy is taken based on the results of these tests.
...more
Total knee replacement
My mom suffers from gonarthrosis for the past three years. Despite treatment by injections the pain is still present. MRI revealed a meniscal tear in the posterior horn, the presence of small bony osteophytes on the patella, a small amount of fluid in the joint cavity (signs of exudative synovitis were detected)
joint space is asymmetrically narrowed in the medial segment. The pain is ongoing but the knee remains flexible. Tell me, please, whether the surgery is contraindicated for meniscal tear in case of arthrosis? Is it possible to do an arthroscopic surgery on the meniscus in our case or it should be «major» surgery? And what would you advice concerning knee replacement for the patient in the age of 57? What is the life time of the artificial joint?
...more It is necessary to make an X-ray of the knee in direct projection in standing position. If it turns out that there is no medial cartilage in the medial area, then the knee replacement is the only solution. The age of 57 is normal for the prosthetics. Modern artificial knee joint (when properly placed of course) will
serve for a lifetime. You can make an appointment via phone +7 (495) 933-66-44.
...more 
Kardanov Andrey
07 September 2016
Pain
I am 19 years old, professionally engaged in weightlifting. I did an arthroscopy of both knee joint a year ago, now feel pain in them and it prevents me from training at full capacity. I visited a traumatologist, and «osteoarthritis of 1 degree» was diagnosed. Could you advise me some medicines or anything else to
relief the pain? Thank you very much for the answer!
...more
First of all you should undergo an MRI and find out what was done at arthroscopy; if it’s really an arthrosis of 1 degree, hyaluronic acid injections are possible and physiotherapy is not required. Anyway, you are always welcome to consultation for thorough examination.
Question to Dr. Yakobashvili
Tell me, please, at which age child's hearing should be checked-up if we were informed at the hospital before discharge that one ear does not hear. At the moment the child’s age is 1.5 months. Thank you.
These tests done in the hospital are often false negative. Hearing can be tested now, it is necessary to make an appointment to the audiologist.
Cought
A child of 11 years old, suffers from cough for more than six months. The cough is dry, sometimes attack-like, mainly begins during the day, and often occurs before sleep. There is no cough at night. CBC is normal, glucose is 4.16, total IgE 111.80, Toxocara, Ascaride are negative, Cytomegalovirus, Mycoplasma are
negative, PPD test is negative as well. A chest x-ray is normal. We have already consulted with a therapist, otolaryngologist, pulmonologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist... the cough is still present. What should we do?
...more First of all, there are no results of whooping cough testing among the results provided above. The disease cannot be ruled out, even if your child was vaccinated. The blood test for antibodies against the whooping cough germ is required (blood test for class M and G antibodies against Bordetella pertussis). Second,
even a slight increase in class E antibodies is a reason to visit an allergist and to perform an evaluation of respiratory function with bronchodilator. This method will detect a latent bronchial spasm in your child. Even if the results of the test will be normal, allergologist mast rule out the allergic nature of the cough even if it's not obstructive syndrome. Third, this cough can be due to gastroesophageal reflux. It is difficult to draw any conclusions having no data of gastroenterologist’s consultation. 24-hour acidity monitoring of the stomach and esophagus is carried out to confirm or exclude the presence of reflux. Fourth, you didn’t mention whether x-ray of nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses was done. Perhaps, after all, the pathology is associated with ENT organs.
...more 
















.webp)

.webp)





